Rupsa Upazila
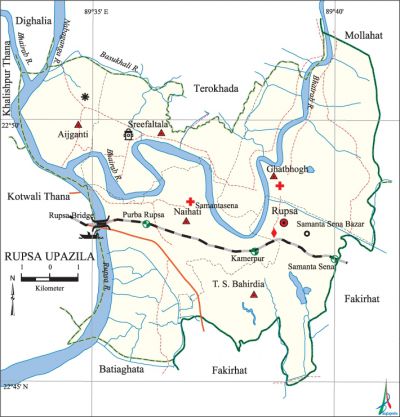
Rupsa Upazila (khulna district) area 120.15 sq km, located in between 22°43' and 22°52' north latitudes and in between 89°33' and 89°41' east longitudes. It is bounded by terokhada upazila on the north, fakirhat and batiaghata upazilas on the south, mollahat and Fakirhat upazilas on the east, kotwali (Khulna) and khalishpur thanas on the west.
Population Total 179519; male 90189, female 89330; Muslim 152641, Hindu 26494, Christian 345 and others 39.
Water bodies Main rivers: rupsa, bhairab, nabaganga, Basukhali.
Administration Rupsa upazila was formed in 1983.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| - | 5 | 64 | 78 | 7101 | 172418 | 1494 | - | 58.2 |
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area |
Mouza |
Population |
Density (per sq km |
Literacy rate (%) | ||||
| 2.93 | - | 7101 | 2424 | - | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
| Aijganti 13 | 2383 | 22313 | 22005 | 60.6 |
| Ghatbhogh 27 | 12652 | 16894 | 16892 | 53.7 |
| T. S. Bahirdia 81 | 4086 | 9102 | 8772 | 64.6 |
| Naihati 54 | 6713 | 29084 | 29215 | 59.7 |
| Sreefaltala 67 | 3870 | 12796 | 12446 | 52.1 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
War of Liberation The Pak army conducted mass killing and heavy plundering in the upazila in 1971. They also set many houses on fire. On 10 November the Indian Air Force mistakenly launched an attack and destroyed two war ships named ‘Padma’ and ‘Palash’ belonging to the freedom fighters. The Artificer of Palash, Bir Srestha ruhul amin, jumped into the river with burn injury but was killed by the razakars on his way to the river bank. Two memorial monuments (on the graveyards of Bir Srestha Ruhul Amin and Bir Bikram Mohibullah) were built in the upazila.
For details: See রূপসা উপজেলা, বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation Bangla Version), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ৯।
Religious institutions Mosque 175, temple 56, church 2. Noted religious institutions: Rupsa Jami Mosque, Aijganti Jami Mosque, Senerpukur Jami Mosque.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 58.2%; male 60.9%, female 55.6%. Educational institutions: college 7, secondary school 5, primary school 65, brac operated school 38, satellite school 5, madrasa 11, orphanage 6. Noted educational institutions: Bangabandhu College (1972), Rupsa College (1986), Ajgara High School (1898), Naihati Secondary School (1920), Befulia Secondary School (1947), Rupsa Girls' High School, Kajdia Madrasa, Baghmara Al Aksha Dakhil Madrasa, Nandanpur Dakhil Madrasa.
Cultural organisations Library 5, cinema hall 1, theatre stage 2, club 21, women organisation 25.
Main sources of income Agriculture 24.99%, non-agricultural labourer 16.57%, industry 1.86%, commerce 21.14%, transport and communication 5.97%, service 13.87%, construction 2.26%, religious service 0.21%, rent and remittance 0.48% and others 12.65%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 37.75%, landless 62.25%.
Main crops Paddy, jute, maskalai, mustard, ground-nut, potato, ginger, vegetables.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Tobacco, sugarcane.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, blackberry, banana, papaya, pineapple, coconut, betel nut, guava, litchi, lemon.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 121, dairy 40, poultry 65.
Communication facilities Pucca road 149 km, semi-pucca road 125 km, mud road 446 km. Rupsa Bridge is notable.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, bullock cart, horse carriage.
Noted manufactories Dockyard 15, saw mill 25, brick-field 30, salt factory 11, rice mill 21, ice factory 10.
Cottage industries Goldsmith 21, blacksmith 21, potteries 61, conch bangle industry 73, wood work 21.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 15, fairs 3, most noted of which are Sener Bazar, Paler Bazar, Natun Hat at Naihati, Rupsa Bazar, Samanta Sena Bazar, Mochabbarpur Bazar, Alaipur Hat, Shiali Mela and Bandakhal Mela.
Main exports Shrimp, betel nut, vegetables.
Access to electricity All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 75.8% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 97.7%, tap 0.7% and others 1.6%.
Sanitation 76.4% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 21.9% of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 1.7% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Hospital 2, upazila health complex 1, upazila family planning clinic 1, union health and family welfare centre 5, community clinic 20.
Natural disasters The floods and cyclones of 1988 and 1998 caused heavy damages to fishery, livestock, and crops of the upazila.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are asa, brac, proshika, Jagrata Jubo Sangha. [Ashraful Islam Goldar]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Rupsa Upazila 2007.
