Hatibandha Upazila
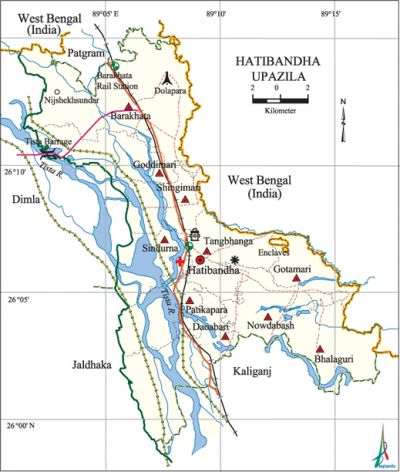
Hatibandha Upazila (lalmonirhat district) area 288.42 sq km, located in between 25°59' and 26°16' north latitudes and in between 89°01' and 89°17' east longitudes. It is bounded by patgram upazila on the north and west bengal state of India, kaliganj (lalmonirhat) upazila on the south, West Bengal state of India on the east, dimla and jaldhaka upazilas on the west.
Population Total 206276; male 104964, female 101312; Muslim 178129, Hindu 27999, Buddhist 8 and others 140. Indigenous communities such as santal and garo belong to this upazila.
Water bodies Main river: tista.
Administration Hatibandha Thana was formed in 1914 and it was turned into an upazila' on 15 April 1983.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
|
- |
10 |
63 |
65 |
23975 |
182301 |
715 |
45.5 |
38.5 |
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area |
Mouza |
Population |
Density |
Literacy rate | ||||
|
18.29 |
4 |
23975 |
1311 |
45.5 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
|
Goddimari 38 |
5805 |
8202 |
8007 |
38.84 |
|
Gotamari 47 |
5234 |
9818 |
9566 |
42.86 |
|
Tangbhanga 95 |
6557 |
13719 |
12794 |
42.40 |
|
Daoabari 28 |
9474 |
8958 |
8517 |
31.38 |
|
Nowdabash 57 |
4718 |
8375 |
8279 |
38.44 |
|
Patikapara 66 |
5575 |
5269 |
5269 |
30.79 |
|
Barakhata 09 |
16579 |
23254 |
22617 |
42.09 |
|
Bhalaguri 19 |
6686 |
10659 |
10205 |
36.99 |
|
Shingimari 76 |
5533 |
10850 |
10408 |
41.81 |
|
Sindurna 85 |
5109 |
5860 |
5660 |
36.37 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001,Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Five domed mosque like house (eighteenth century).
History of the War of Liberation On 9 March 1971, the flag of Bangladesh was hoisted in a gathering at the premises of the Hatibandha Dakbangalow. On 8 April, the Pak army took control over Hatibandha; on the same day they captured a number of people and brutally killed them at a place adjacent to the Barakhata Bus stand. On 19 November the freedom fighters raided Barakhata. The Pak soldiers were forced to surrender in the face of heavy attack of the freedom fighters on 28 and 29 November. Hatibandha was liberated on 30 November.
Marks of the War of Liberation Mass grave 5, martyr' memorial 4.
Religious institutions Mosque 343, temple 57, church 2, sacred place 1, tomb 2. Noted religious institutions: Tomb of Garibullah Shah.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 39.3%; male 45.3%, female 33.1%. Educational institutions: college 4, secondary school 36, primary school 110, madrasa 56. Noted educational institutions: Alimuddin Degree College (1970), Hatibandha Mohila College (1995), Barakhata College (1999), Hatibandha S. S High School (1946), Barakhata High School (1952), Goddimari Bilateral High School (1961), Nowdabash K. M. S. C High School (1973), Hatibandha Adarsha High School (1994), Bhabanipur Chhafatia Senior Madrasa (1954), Hatibandha Alim Madrasa (1979).
Cultural organisations Library 24, theatre group 3, cinema hall 4, club 15.
Tourist spots Tista Barrage, Shalban.
Main sources of income Agriculture 78.02%, non-agricultural labourer 2.71%, industry 0.26%, commerce 8.14%, transport and communication 2.50%, service 3.16%, construction 0.62%, religious service 0.18%, rent and remittance 0.10% and others 4.31%.
Main crops Paddy, jute, wheat, tobacco, potato, nut, bay leaf, nipa palm, onion, garlic, vegetables.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Mustard, kaun, sesame, linseed, sugarcane, arahar, barley, sweet potato.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, banana, guava, papaya, elephant apple, coconut, indian jujube, betel nut.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 514, dairy 12, poultry 60, hatchery 8.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, bullock cart, horse carriage.
Noted manufactories Saw mill, ice factory, bidi factory.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, blacksmith, weaving, bamboo work.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 13, fairs 10, most noted of which are Hatibandha Hat, Barakhata Hat, Doi Khaor Hat, Parulia Hat, Ketkibari Hat; Kazir Bazar and Nowdabash Baddanath Mela, Shibratri Mela, Dhaolai Mela and Parulia Troadashi Mela.
Main exports Tobacco, bay leaf, nipa palm, onion, garlic, banana, flour.
Access to electricity All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 3.60% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Natural resources Stone and sand composed of high quality silicate and manganese has been discovereed in this upazila.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 89.78%, tap 0.35%, pond 0.36 and others 9.50%.
Sanitation 20.51% (rural 17.10% and urban 47.32%) of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 38.21% (rural 41.03% and urban 16.06%) of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 41.28% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, union health centre 2.'
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are brac, RDRS. [SM Altaf Hossain]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Hatibandha Upazila 2007.
