Langadu Upazila
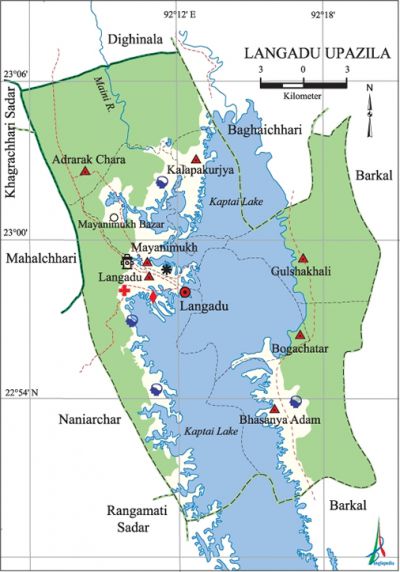
Langadu Upazila (rangamati district) 'area 388.5 sq km, located in between 22°48' and 23°06' north latitudes and in between 92°05' and 92°19' east longitudes. It is bounded by baghaichhari and dighinala (khagrachhari) upazilas on the north, barkal upazila on the south and the east, rangamati sadar, naniarchar, mahalchhari and khagrachhari sadar upazilas on the west.
Population Total 68014; male 35955, female 32059; Muslim 49251, Hindu 1019, Buddhist 146, Christian 17593 and others 5. Indigenous communities such as chakma, tripura and Pangkhoa belong to this upazila.
Water bodies Main river: Maini; kaptai lake occupies about one third area of the upazila.
Administration Langadu Thana, now an upazila, was formed in 1909.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
|
- |
7 |
25 |
135 |
14912 |
53102 |
175 |
47.1 |
32.5 |
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Mouza |
Population |
Density (per sq km) |
Literacy rate (%) | ||||
|
85.47 |
2 |
14912 |
174 |
47.09 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
|
Adrarak Chara 13 |
19200 |
5427 |
4622 |
34.23 |
|
Kalapakurjya 60 |
1319 |
3094 |
3037 |
24.09 |
|
Gulshakhali 54 |
2560 |
3899 |
3664 |
31.05 |
|
Bogachatar 40 |
15360 |
5386 |
4842 |
32.66 |
|
Bhasanya Adam 27 |
17920 |
3635 |
3153 |
38.79 |
|
Mayanimukh 81 |
1520 |
7508 |
6377 |
41.68 |
|
Langadu 67 |
35840 |
7006 |
6364 |
39.36 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
History of the War of Liberation In 1971 the Pak soldiers conducted mass killing and indiscriminate plundering in this upazila; they also set many houses on fire. Direct encounters were held between the freedom fighters and the Pak army at Ambagan and Rangipara of the present Bogachatar union. Langadu was liberated on 6 December.
Marks of the War of Liberation Memorial monument 1.
Religious institutions Mosque 58, temple 7, church 4, pagoda 7. Noted religious institutions: Mayanimukh Central Jami Mosque, Rabeta Hospital Jami Mosque, Adrarak Chara Church.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 35.8%; male 43.5%, female 27.1%. Educational institutions: college 1, secondary school 21, primary school 72, community school 4, madrasa 10, orphanage 4. Noted educational institutions: Rabeta Model College (1995), Langadu Government High School, Langadu Girls' High School, Rabeta Model High School, Kattali High School, Gulshakhali High School, Mayanimukh Islamia Fazil Madrasa.
Cultural organisations Library 3, club 48, press club 1, eidgah 19, cinema hall 1, shilpakala academy 1, women organisation 10, playground 12.
Tourist spots Banasree Rest House (1900), Longadu Forest, Tin Tila Forest (1970), Dulchhari Jet Resort (2000), Ganthachhara' Baitus Sharaf Complex, Rest House of Rabeta Hospital.
Main sources of income Agriculture 69%, non-agricultural labourer 5.35%, commerce 9.27%, service 5.95%, construction 0.60%, religious service 0.30%, rent and remittance 1.18% and others 8.35%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 68.87%, landless 31.13%; agricultural landowner: urban 75.46% and rural 43.12%.
Main crops Paddy, maize, pulse, cotton, tobacco, potato, sugarcane.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Mustard, kaun.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, litchi, banana, coconut, pineapple, papaya.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 115, dairy 10, poultry 16.
Communication facilities Pucca road 3 km, semi-pucca road 21 km, mud road 50 km; waterway 50 nautical miles.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, bullock cart.
Noted manufactories Rice mill, flour mill, textile mill, brick-field, food processing factory, welding factory.
Cottage industries Goldsmith 16, blacksmith 12, weaving 1632, wood work 117, bamboo and cane work 75.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 12, most noted of which are Bara Mayanimukh Bazar, Karallachhari Bazar, Boiragi Bazar, Kattali Hat and Bhaibon Chhara Hat.
Main exports Wood, jackfruit, pineapple, tobacco.
Health centres Hospital 3, satellite clinic 2, upazila health complex 1, family planning centre 6, community clinic 7, veterinary hospital 1.
Natural disasters Many people were victims of the devastating cyclone on 29 April 1991; it also caused heavy damages to settlements, livestock, crops and other properties of the upazila.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are CCRDB. [Gautam Chandra Modak]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Langadu Upazila 2007.
