Baliakandi Upazila: Difference between revisions
(Content Updated.) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
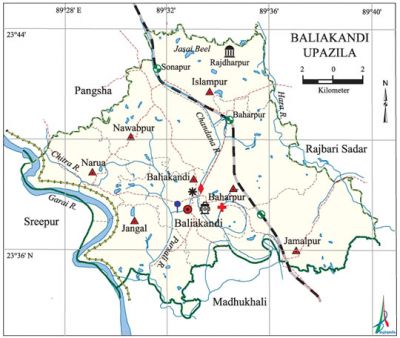
'''Baliakandi Upazila''' ([[Rajbari District|rajbari district]]) area | '''Baliakandi Upazila''' ([[Rajbari District|rajbari district]]) area 228.99 sq km, located in between 23°33' and 23°44' north latitudes and in between 90°26' and 90°40' east longitudes. It is bounded by [[Pangsha Upazila|pangsha]] upazila on the north, [[Madhukhali Upazila|madhukhali]] upazila on the south, [[Rajbari Sadar Upazila|rajbari sadar]] upazila on the east, Pangsha and [[Sreepur Upazila (Magura District)|sreepur]] upazilas on the west. | ||
''Population'' Total | ''Population'' Total 207086; male 103675, female 103411; Muslim 164206, Hindu 42819, Christian 57, Buddhist 3 and others 1. | ||
''Water bodies'' Main rivers: Hara, [[Chitra River|chitra]], Chandana, Gorai, Pursali; Sreehar Beel, Jasai Beel and Rajapur Canal are notable. | ''Water bodies'' Main rivers: Hara, [[Chitra River|chitra]], Chandana, Gorai, Pursali; Sreehar Beel, Jasai Beel and Rajapur Canal are notable. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| Urban || Rural || | Urban || Rural | | Urban || Rural || | Urban || Rural | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | - || 7 || 150 || 258 || 9897 || 197189 || 904 || 66.9 || 54.9 | ||
- | |||
| | |||
7 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
258 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
{| class="table table-bordered table-hover" | {| class="table table-bordered table-hover" | ||
|- | |- | ||
| Line 51: | Line 24: | ||
Area<br> | Area<br> | ||
(sq km) | (sq km) | ||
| | | | ||
Mouza | Mouza | ||
| | | | ||
Population | Population | ||
| | | | ||
Density<br> | Density<br> | ||
(per sq km) | (per sq km) | ||
| | | | ||
Literacy rate<br> | Literacy rate<br> | ||
(%) | (%) | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 5.63 (2001) || 3 || 9897 || 1271 (2001) || 66.9 | ||
5.63 | |||
| | |||
3 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
1271 | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
{| class="table table-bordered table-hover" | {| class="table table-bordered table-hover" | ||
| colspan="5" | Union | | colspan="5" | Union | ||
| Line 91: | Line 44: | ||
| Male || Female | | Male || Female | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Islampur 47 || 8232 || 15306 || 15664 || 53.6 | ||
Islampur 47 | |||
| | |||
8232 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Baharpur 17 || 9342 || 17451 || 17039 || 55.0 | ||
Baharpur | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Baliakandi 19 || 6324 || 13776 || 13821 || 54.5 | ||
Baliakandi 19 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Jamalpur 57 || 9794 || 15212 || 14884 || 57.9 | ||
Jamalpur 57 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Jangal 66 || 7236 || 10253 || 10048 || 54.1 | ||
Jangal 66 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Narua 85 || 6113 || 12769 || 12984 || 54.4 | ||
Narua 85 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Nawabpur 95 || 9545 || 18908 || 18971 || 57.6 | ||
Nawabpur 95 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
''Source'' Bangladesh Population Census | ''Source'' Bangladesh Population Census 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics. | ||
[[Image:BaliakandiUpazila.jpg|thumb|400px|right]] | [[Image:BaliakandiUpazila.jpg|thumb|400px|right]] | ||
''Archaeological heritage and relics'' Kalyandighi (Rajdharpur, excavated in 1465), Jorbangla Hindu Mandir (Nalia, 17th century), Sanadhi Nagar Math (Jangalbari, 19th century). | ''Archaeological heritage and relics'' Kalyandighi (Rajdharpur, excavated in 1465), Jorbangla Hindu Mandir (Nalia, 17th century), Sanadhi Nagar Math (Jangalbari, 19th century). | ||
''Historical events'' Baliakandi was | ''Historical events'' Baliakandi was one of the major centres of [[Fakir-Sannyasi Resistance|fakir-sannyasi resistance]] movement. The peasants of village Sonapur led the indigo resistance movement. | ||
'' | ''War of Liberation'' Freedom fighters of the upazila had an encounter with the razakars and police forces at Baliakandi in November during the [[War of Liberation, The|war of liberation]]; the collaborators were defeated and Surrendered, and all their arms and ammunitions were captured by the freedom fighters. There is a mass grave at Baharpur and a mass killing site at Ramdia of Balikandi upazila. | ||
For details: see বালিয়াকান্দি উপজেলা, ''বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ'' (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ৭। | |||
''Religious institutions'' Mosque 152, temple 113, tomb 10, sacred place 1. | ''Religious institutions'' Mosque 152, temple 113, tomb 10, sacred place 1. | ||
''Literacy rate and educational institutions'' Average literacy | ''Literacy rate and educational institutions'' Average literacy 55.5%; male 57.1%, female 53.8%. Educational institutions: college 4, secondary school 21, primary school 88, madrasa 5. Noted educational institutions: Bakshabhangi Government Primary School (1894), Patra Government Primary School (1919). | ||
''Cultural organisations'' Library 9, club 11, theatre stage 2, theatre group 5, women organisation 2, cinema hall 4, playground 8. | ''Cultural organisations'' Library 9, club 11, theatre stage 2, theatre group 5, women organisation 2, cinema hall 4, playground 8. | ||
| Line 227: | Line 85: | ||
''Fisheries, dairies and poultries'' Fishery 19, dairy and poultry 111. | ''Fisheries, dairies and poultries'' Fishery 19, dairy and poultry 111. | ||
''Communication facilities'' Roads: pucca 138 km, semi-pucca 69 km, mud road 445 km; railway 20 km; waterway 26 km. | |||
''Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport'' Palanquin, duli, horse carriage. | ''Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport'' Palanquin, duli, horse carriage. | ||
| Line 236: | Line 96: | ||
''Main exports'' Jute, sugarcane, oil seeds, catechu. | ''Main exports'' Jute, sugarcane, oil seeds, catechu. | ||
''Access to electricity'' All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However | ''Access to electricity'' All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 39.4% of the dwelling households have access to electricity. | ||
''Sources of drinking water'' Tube-well | ''Sources of drinking water'' Tube-well 95.8%, tap 0.2% and others 4.0%. | ||
''Sanitation'' | ''Sanitation'' 81.0% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 15.5% of dwelling houses use non-sanitary latrines; 3.5% of households do not have latrine facilities. | ||
''Health centres'' Upazila health centre 1, satellite clinic 6, family planning centre 3. | ''Health centres'' Upazila health centre 1, satellite clinic 6, family planning centre 3. | ||
| Line 246: | Line 106: | ||
''NGO activities'' Operationally important NGOs are [[BRAC|brac]], [[ASA|asa]]. [Badrul Alam Tipu] | ''NGO activities'' Operationally important NGOs are [[BRAC|brac]], [[ASA|asa]]. [Badrul Alam Tipu] | ||
'''References'''' Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Baliakandi Upazila 2007. | '''References'''' Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Baliakandi Upazila 2007. | ||
[[Category:Upazilas of Bangladesh]] | [[Category:Upazilas of Bangladesh]] | ||
Latest revision as of 17:33, 26 October 2023
Baliakandi Upazila (rajbari district) area 228.99 sq km, located in between 23°33' and 23°44' north latitudes and in between 90°26' and 90°40' east longitudes. It is bounded by pangsha upazila on the north, madhukhali upazila on the south, rajbari sadar upazila on the east, Pangsha and sreepur upazilas on the west.
Population Total 207086; male 103675, female 103411; Muslim 164206, Hindu 42819, Christian 57, Buddhist 3 and others 1.
Water bodies Main rivers: Hara, chitra, Chandana, Gorai, Pursali; Sreehar Beel, Jasai Beel and Rajapur Canal are notable.
Administration Baliakandi Thana was formed in 1881 and it was turned into an upazila in 1983.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| - | 7 | 150 | 258 | 9897 | 197189 | 904 | 66.9 | 54.9 |
| Upazila Town | ||||
|
Area |
Mouza |
Population |
Density |
Literacy rate |
| 5.63 (2001) | 3 | 9897 | 1271 (2001) | 66.9 |
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
| Islampur 47 | 8232 | 15306 | 15664 | 53.6 |
| Baharpur 17 | 9342 | 17451 | 17039 | 55.0 |
| Baliakandi 19 | 6324 | 13776 | 13821 | 54.5 |
| Jamalpur 57 | 9794 | 15212 | 14884 | 57.9 |
| Jangal 66 | 7236 | 10253 | 10048 | 54.1 |
| Narua 85 | 6113 | 12769 | 12984 | 54.4 |
| Nawabpur 95 | 9545 | 18908 | 18971 | 57.6 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Kalyandighi (Rajdharpur, excavated in 1465), Jorbangla Hindu Mandir (Nalia, 17th century), Sanadhi Nagar Math (Jangalbari, 19th century).
Historical events Baliakandi was one of the major centres of fakir-sannyasi resistance movement. The peasants of village Sonapur led the indigo resistance movement.
War of Liberation Freedom fighters of the upazila had an encounter with the razakars and police forces at Baliakandi in November during the war of liberation; the collaborators were defeated and Surrendered, and all their arms and ammunitions were captured by the freedom fighters. There is a mass grave at Baharpur and a mass killing site at Ramdia of Balikandi upazila.
For details: see বালিয়াকান্দি উপজেলা, বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ৭।
Religious institutions Mosque 152, temple 113, tomb 10, sacred place 1.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 55.5%; male 57.1%, female 53.8%. Educational institutions: college 4, secondary school 21, primary school 88, madrasa 5. Noted educational institutions: Bakshabhangi Government Primary School (1894), Patra Government Primary School (1919).
Cultural organisations Library 9, club 11, theatre stage 2, theatre group 5, women organisation 2, cinema hall 4, playground 8.
Main sources of income Agriculture 71.4%, non-agricultural labourer 2.27%, industry 0.48%, commerce 11.9%, transport and communication 3.2%, service 4.68%, construction 0.9%, religious service 0.16%, rent and remittance 0.27% and others 4.74%.
Main crops Paddy, jute, sugar cane, oil seeds, catechu.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Cotton, jaffron.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, coconut, banana.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 19, dairy and poultry 111.
Communication facilities Roads: pucca 138 km, semi-pucca 69 km, mud road 445 km; railway 20 km; waterway 26 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, duli, horse carriage.
Cottage industries Blacksmith, potteries, wood work, bamboo work, nakshi kantha, nakshi pakha.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 6, fairs 5; most noted of which are Baharpur, Jamalpur, Sonapur, Baliakandi hats and Mela of Hari Thakur and Beruli Mela.
Main exports Jute, sugarcane, oil seeds, catechu.
Access to electricity All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 39.4% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 95.8%, tap 0.2% and others 4.0%.
Sanitation 81.0% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 15.5% of dwelling houses use non-sanitary latrines; 3.5% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health centre 1, satellite clinic 6, family planning centre 3.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are brac, asa. [Badrul Alam Tipu]
References' Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Baliakandi Upazila 2007.
