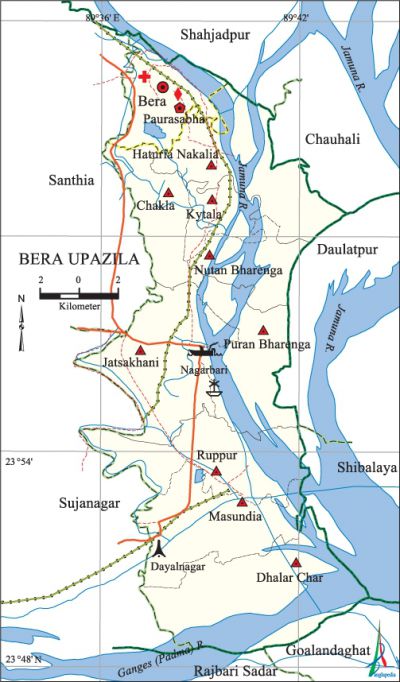
Bera Upazila
Bera Upazila (pabna district) area 243.43 sq km, located in between 23°48' and 24°06' north latitudes and in between 89°35' and 89°44' east longitudes. It is bounded by shahjadpur and chauhali upazilas on the north, goalanda and rajbari sadar upazilas on the south, Chauhali, daulatpur and shivalaya upazilas on the east, sujanagar and santhia upazilas on the west.
Population Total 256793; male 128397, female 128396; Muslim 246463, Hindu 10320, Christian 4 and others 6.
Water bodies Main rivers: padma, jamuna, ichamati and hurasagar; Dhalai beel, Ichar beel and Nandiar beel are notable.
Administration Mathura Thana was formed in 1828 and was shifted to Bera in 1927 after it got submerged by river erosion. Bera thana was turned into an upazila in 1983.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| 1 | 9 | 130 | 162 | 50068 | 206725 | 1055 | 52.2 | 38.5 |
| Municipality | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Ward |
Mahalla |
Population |
Density |
Literacy rate (%) | |||
| 16.42 | 9 | 26 | 50068 | 3049 | 52.2 | |||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
| Kytala 47 | 2333 | 6798 | 7073 | 42.0 |
| Chakla 15 | 3638 | 7719 | 7352 | 40.1 |
| Jatsakhni 42 | 8579 | 26473 | 26090 | 46.2 |
| Dhalar Char 21 | 9406 | 9209 | 8645 | 14.9 |
| Nutan Bharenga 63 | 3254 | 9910 | 10348 | 36.2 |
| Puran Bharenga 73 | 6531 | 6125 | 6081 | 34.6 |
| Masundia 52 | 7131 | 11325 | 11224 | 40.3 |
| Ruppur 84 | 7354 | 9152 | 9073 | 41.0 |
| Haturia Nakalia 31 | 7412 | 16568 | 17560 | 36.3 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
War of Liberation On 31 March 1971 the freedom fighters resisted the Pak army at the Nagarbari Ferry Ghat. A number of innocent civilians were killed while the Pak army conducted air raid on 9 April in order to dislodge the freedom fighters. On 19 April a battle was fought between the freedom fighters and the Pak army at Paikarhati (a border place between Bera and Santiha) on the Nagarbari-Bogra highway in which 25 freedom fighters and 150 Pak soldiers were killed. During the period between July and August the Naksals attacked he freedom fighters and captured 57 rifles. Bera was liberated on 14 December 1971. Mass killing sites had been discovered at Charpara and Dayalnagar and there is a mass grave at Dayalnagar; a memorial sculpture has been built at Paikarhat.
For details: see বেড়া উপজেলা, বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ৭।
Religious institutions Mosque 155, temple 43. Noted religious institutions: Dargabari Mosque, Bera Bazar Jami Mosque and Buromata Temple, Haribari Temple.
Literacy and educational institutions Average literacy 41.2%; male 44.2%, female 38.3%. Educational institutions: college 6, secondary school 16, primary school 104, kindergarten 15, madrasa 20. Noted educational institutions: Bera Degree College (1964), Bharenga Academy (1858), Bera BB High School (1899), Bera High School (1906), Dhobakhola Coronation High School (Natiabari, 1912), Nakalia Sandashia Banik High School (1919), Vocational BB School, Vocational Bera Pilot Girls' School, Bera Alim Madrasa (1938).
Newspapers and periodicals Weekly: A Juger Dwip.
Cultural organisations Club 26, library 3, theatre group 1, cinema hall 2, auditorium 3, playground 1.
Main sources of income Agriculture 40.07%, non-agricultural labourer 3.94%, industry 7.92%, commerce 21.80%, transport and communication 4.92%, service 5.77%, construction 1.08%, religious service 0.21%, rent and remittance 0.48% and others 13.81%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 44.60%, landless 55.40%; agricultural landowner: urban 28.52% and rural 48.42%.
Main crops Paddy, wheat, sugarcane, mustard seed, onion, garlic, potato, vegetables.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Sesame, bhura, kaun, jute, china, cotton, sweet potato.
Main fruits Mango, black berry, guava, banana.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries This upazila has a number of fisheries, dairies and poultries.'
Communication facilities Pucca road 131 km, semi pucca road 15, mud road 156 km; waterway 25 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, Dhuli, bullock cart, buffalo cart.
Noted manufactories Flour mill, ice factory, welding factory.
Cottage industries Handloom, bamboo work, wood work,.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 17, fairs 3, most noted of which are Bera Hat and Bazar, Bander Hat, Chatur Hat, Khanpura Hat, Mahakal Bhairavi Mela (Khanpura Bazar) and Raksa Bazar Mela.
Main exports Lungi, onion, garlic, sugarcane molasses.
Access to electricity All the wards and unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 70.8% dwellings have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 96%, tap 2.2% and others 1.8%.
Sanitation 62.4% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 35.5% of dwelling houses use non-sanitary latrines; 2.1% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, family planning center 5, charitable dispensary 1, clinic 1.
Natural Disasters' The floods of 1988 and 1989 caused huge damages to settlements and crops of the upazila.
NGO activities brac, asa. [Abdus Sattar]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Bera Upazila 2007.
