Chandina Upazila
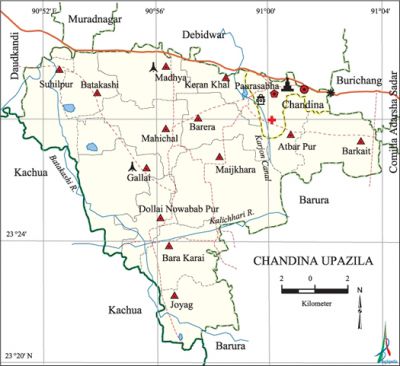
Chandina Upazila (comilla district) area 201.92 sq km, located in between 23°21' and 23°31' north latitudes and in between 90°51' and 91°04' east longitudes. It is bounded by daudkandi, muradnagar and debidwar upazilas on the north, barura and kachua (chandpur) upazilas on the south, burichang, comilla adarsha sadar and Barura upazilas on the east, Daudkandi and Kachua upazilas on the west.
Population Total 306054; male 154160, female 151894; Muslim 282936, Hindu 23078, Buddhist 15 and others 25.
Water bodies Kalichhari and Batakashi rivers, Karjon Canal and Ghograr Beel are notable.
Administration Chandina Thana was turned into an upazila in 1983.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
|
1 |
13 |
126 |
222 |
37700 |
268354 |
1516 |
49.11 |
43.23 |
| Municipality | ||||||||
|
Area |
Ward |
Mahalla |
Population |
Density |
Literacy rate | |||
|
13.23 |
9 |
19 |
36151 |
2732 |
42.37 | |||
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area |
Mouza |
Population |
Density |
Literacy rate | ||||
|
0.75 |
- |
1549 |
2065 |
40.85 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
|
Atbar Pur 47 |
1764 |
3444 |
3452 |
43.43 |
|
Keran Khal 13 |
2411 |
7081 |
7087 |
46.44 |
|
Gallai 55 |
5024 |
15120 |
14390 |
41.77 |
|
Joyag 31 |
3474 |
10339 |
10847 |
50.11 |
|
Dollai Nowabab Pur 63 |
2515 |
10489 |
10047 |
46.78 |
|
Barkait 39 |
3900 |
10882 |
10967 |
40.71 |
|
Bara Karai 23 |
3731 |
10038 |
10192 |
39.18 |
|
Barera 15 |
2762 |
8210 |
8326 |
40.96 |
|
Batakashi 87 |
3670 |
8781 |
9029 |
41.44 |
|
Mahichal 20 |
3673 |
9602 |
9303 |
49.90 |
|
Maijkhara 79 |
7520 |
21047 |
21035 |
41.03 |
|
Madhya 71 |
3524 |
12000 |
11325 |
41.73 |
|
Suhilpur 94 |
3521 |
8412 |
8458 |
42.03 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Raj Kachary (revenue office), Kali Mandir (Chandina), Mazar of Hazrat Hober Ali (R) at Arikhola.
History of the War of Liberation On 11 December 1971, in a direct encounter between the Pak army and the freedom fighters nearly 1400 Pak soldiers surrendered to the freedom fighters. In another direct encounter at Kat-tala on 12 December seven members of the Pak army were killed and so were three freedom fighters. Besides, 6 freedom fighters were killed and nearly 23 were wounded in an encounter with the Pak army at Fawi of Chandina.
Marks of War of Liberation Mass killing site 2 (Puira Bridge east of Chandina High School and the northwest side of the Chandina Hospital); Mass grave 3: Shashan Ghat (crematorium) at Kashimpur, Baroi Para at Mahichail and Barabari at Konghai.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 43.97%; male 34.30%, female 40.28%. Educational institutions: college 5, secondary school 32, primary school 116, madrasa 49. Noted educational institutions: Kailain Tulpai High School (1913), Chandina Pilot High School (1916), Dollai Nowabab Pur High School (1939), Madhya Bazar Chhadim High School (1943), Bishwas Government Primary School (1916), Madhya Government Primary School (1930), Paschim Belashar Government Primary School (1935), Barakhat Government Primary School (1939), Chandina Model Government Primary School (1940), Khirasar Mohanpur Dakhil Madrasa (1987).
Cultural organisations Club 52, library 4, cinema hall 1, theatre stage 1.
Main sources of income Agriculture 56.71%, non-agricultural labourer 2.46%, commerce 14.07%, transport and communication 4.54%, service 8.24%, construction 1.13%, religious service 0.46%, rent and remittance 3.91% and others 8.48%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 65.17%, landless 34.83%; agricultural landowner:' urban 45.95% and rural 67.82%.
Main crops Paddy, wheat, potato, mustard, vegetables.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Jute, masuri, seasame, linseed, kaun, onion, garlic, tobacco, sugarcane.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, banana, litchi, papaya.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 10, poultry 36, dairy farm 13.
Communication facilities Pucca road 78 km, mud road 139.40 km. Culvert 240.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, bullock cart.
Noted manufactories Textile mill, rice mill, flour mill, oil mill, cold storage.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, weaving, potteries, embroidery, bamboo work, wood work.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 29, fairs 4. Chandina, Madhya, Nowabab Pur and Badarpur hats; Dollai Nowabab Pur, Mahichal, Rasulpur, Rammohan and Kailain bazars; Baraia Krishnapur Arang, Pihar, Madhyamtala and Madhya melas are notable.
''Main exports Khadi cloth, flour, potato.
Access to electricity All the wards and unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 29% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 91.05%, tap 0.67%, pond 3.67% and others 4.61%. The presence of intolerable level of arsenic has been detected in shallow tube-well water of the upazila.
Sanitation 49.87% (rural 51.69% and urban 36.64%) of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 31.83% (rural 29.92% and urban 45.74%) of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 18.29% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, satellite clinic 1, family planning centre 12, hospital 2, union health and family welfare centre 2, clinic 6, diagnostic centre 1.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are brac, asa, proshika. [Muhammad Mosharaf Hossain Bhuiyan]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Chandina Upazila 2007.
