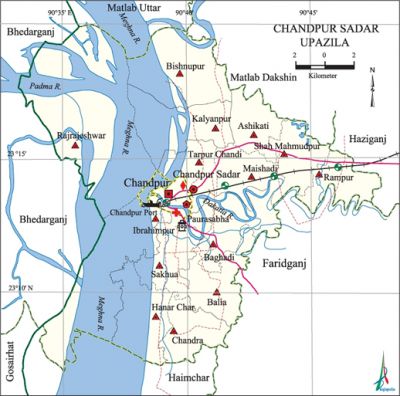
Chandpur Sadar Upazila
Chandpur Sadar Upazila (chandpur district) area 308.78 sq km, located in between 23°07' and 23°20' north latitudes and in between 90°34' and 90°48' east longitudes. It is bounded by matlab dakshin and matlab uttar upazilas on the north, haimchar and faridganj upazilas on the south, hajiganj and Faridganj upazilas on the east, bhedarganj (shariatpur) and gosairhat upazilas on the west.
Population Total 436680; male 220626, female 216054; Muslim 409035, Hindu 26602, Buddhist 342, Christian 59 and others 642. Indigenous community such as Tipra belongs to this upazila.
Water bodies Main rivers: lower meghna, dakatia; Satbaria Beel is notable.
Administration Chandpur Thana was turned into an upazila in 1984. Chandpur Municipality was formed in 1897.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
|
1 |
14 |
146 |
110 |
108558 |
328122 |
1414 |
66.58 |
53.78 |
| Municipality | ||||||||
|
Area |
Ward |
Mahalla |
Population |
Density |
Literacy rate (%) | |||
|
10.59 |
15 |
75 |
91390 |
8630 |
68.16 | |||
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area |
Mouza |
Population |
Density |
Literacy rate (%) | ||||
|
5.58 |
1 |
17168 |
3077 |
57.97 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
|
Ashikati 18 |
3070 |
11881 |
12680 |
56.77 |
|
Ibrahimpur 63 |
11200 |
10364 |
9194 |
49.00 |
|
Kalyanpur 20 |
5507 |
9078 |
9738 |
57.33 |
|
Chandra 54 |
3457 |
15431 |
15527 |
52.62 |
|
Tarpur Chandi 94 |
2743 |
11133 |
10426 |
58.97 |
|
Baghadi 22 |
3398 |
15624 |
14971 |
57.31 |
|
Balia 27 |
4612 |
16959 |
16978 |
53.01 |
|
Bishnupur 31 |
6237 |
14044 |
15508 |
53.81 |
|
Maishadi 67 |
2843 |
12280 |
12065 |
60.81 |
|
Rajrajeshwar 76 |
9760 |
7749 |
7121 |
24.13 |
|
Rampur 85 |
3025 |
10758 |
11064 |
61.97 |
|
Sakhua 90 |
3642 |
22123 |
20871 |
51.51 |
|
Shah Mahmudpur 81 |
3386 |
11298 |
11337 |
61.77 |
|
Hanar Char 58 |
4185 |
4694 |
4394 |
32.07 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Begum Mosque (1812), Kalibari Mandir (1878), Math at Mathkhola. Historical events The coolies of the Assam tea gardens revolted against the atrocities of the British tea garden owners. On their way to Kolkata about 20 thousand coolies assembled at Chandpur steamer ghat. The British government conducted a massacre at the steamer ghat to contain the collies. Hardayal Nag, known as Gandhi of Chandpur, protested against the massacre. This protest movement spread all over the undivided India. Mahatma Gandhi, Maulana Mohammad Ali, chitta ranjan das, and subhas chandra bose visited Chandpur to ease this movement.
Marks of the War of Liberation Sculpture: 'Aungikar'.
Religious institutions Mosque 644, temple 5, church 1, tomb 2. Noted religious institutions: Begum Mosque, Puran Bazar Mosque, tomb of' Khawja Ahmad Saheb (Islampur), Kalibari Mandir.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 57.12%; Male 58.81%, Female 55.43%. Noted educational institutions: Chandpur Govt. College (1946), Chandpur Govt. Mahila College (1964), Puran Bazar Degree College, Hasan Ali Government Boys' High School (former Jubilee High School, 1885), Baburhat High School (1899), Harina-Chalitatali Edward Institution (1901), Chandpur Rupsa Ahamadia High School (1913), Gani Adarsha High School (1917), DN High School (1920), Harisabha Madusadan High school (1921), Puran Bazar M H High School (1921), Kherudia Delowar Hossain High School and College (1925), Sahatali High School (1927), Matreepith Govt. Girls' School (1961), Shahtali Alia Madrasa (1899).
Newspapers and periodicals Daily: Chandpur Barta, Chandpur Probaha, Chandpur Kantha, Chandpur Darpan, Chandpur Zamin, Chandpur Sangbad; Defunct: Nababangha, Bharat Hitoshi, Raktapalash, Raktim Surya.
Cultural organisations Club 81, library 5, cinema hall 3, theatre group 13, women organisation 4, government shishu sadan 1, park 2, stadium 1. Noted cultural organisations: Barnachora (1973, theatre group) and Udayan Mahila Complex (women's organisation).
Important installations Bangladesh Fisheries Research Institute.
Main sources of income Agriculture 33.40%, non-agricultural labourer 3.48%, industry 1.54%, commerce 20.48%, transport and communication 4.44%, service 13.28%, construction 2.75%, religious service' 0.36%, rent and remittance 2.19% and others 18.08%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 46.04%, landless 53.96%; agricultural landowner: urban' 31.75% and rural 50.65%.
Main crops Paddy, sugarcane, jute, potato, wheat.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Sesame, kaun, linseed, china, mustard.'
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, palm, coconut, guava, papaya.'
Fisheries, dairies and poultries This upazila has a number of fisheries, dairies and poultries.
Communication facilities Pucca road 108.92 km, semi-pucca road 4.62 km, mud road 291.62 km; railway 19 km; waterway 28 nautical miles.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, bullock cart.
Noted manufactories Jute mill, rice mill, flour mill, aluminum industries, chemical industries, match industries, ice factory, welding factory.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, blacksmith, potteries, weaving, shital pati, embroidery, bamboo work, cane work.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 28, fairs 5, most noted of which are Baburhat, Mahamaya, Akhaner Hat, Shahtali, Kanudi, Chhoto Sundar, Chandra, Bhagra, Kamranga and Safarmali Hat; Mathkhola Shiva Bari Mela and Mahayamaya Mela.
Main exports Hilsa fish, shrimp, sugarcane, jute and jute products.
Access to electricity All the wards and unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 44.91% (urban 77.42% and rural 34.42%) of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 68.38%, tap 15.67%, pond 11.13% and others 4.82%.
Sanitation 48.70% (urban 69.89% and rural 41.86%) of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 44.86% (urban 25.31% and rural 51.17%) of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 6.44% (urban 4.81% and rural 6.97%) of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Hospital 7, upazila health complex 1, charitable hospital 1, family welfare centre 14, maternity' clinic 2.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are brac, asa, CARE. [Sayeed Ahmed Khan]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Chandpur Sadar Upazila 2007.'
