Chunarughat Upazila
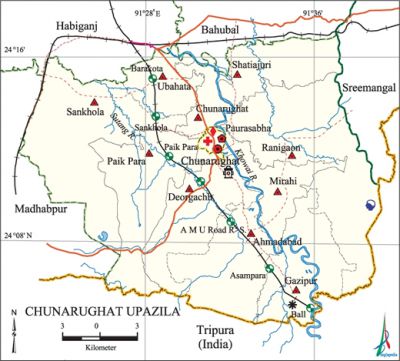
Chunarughat Upazila (habiganj district) area 495.49 sq km, located in between 24°04' and 24°17' north latitudes and in between 91°22' and 91°39' east longitudes. It is bounded by habiganj sadar and bahubal upazilas on the north, tripura state of India on the south, sreemangal upazila and Tripura state of India on the east, madhabpur upazila on the west. The upazila town is well known as an old business centre.
Population Total 267056; male 134840, female 132216; Muslim204738, Hindu 60584, Buddhist 625, Christian 18 and others 1091. Indigenous communities such as khasia, manipuri belong to this upazila.
Water bodies Khowai and Sutang rivers are notable.
Administration Chunarughat Thana was established in 1914 and it was turned into an upazila in 1983.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
|
1 |
10 |
165 |
386 |
8575 |
258481 |
539 |
54.59 |
43.65 |
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area |
Mouza |
Population |
Density |
Literacy rate | ||||
|
3.53 |
3 |
8575 |
2476 |
56.96 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
|
Ahmadabad 09 |
11850 |
14216 |
14040 |
32.13 |
|
Ubahata 95 |
8354 |
10370 |
10356 |
36.97 |
|
Gazipur 38 |
11500 |
15963 |
16095 |
29.57 |
|
Chunarughat 19 |
5001 |
12541 |
12011 |
41.11 |
|
Deorgachh 28 |
11492 |
17358 |
16834 |
37.15 |
|
Paik Para 57 |
11113 |
13301 |
13046 |
26.28 |
|
Mirahi 47 |
8098 |
13314 |
13150 |
31.36 |
|
Ranigaon 66 |
14552 |
13913 |
13609 |
29.03 |
|
Shatiajuri 85 |
8639 |
10295 |
10056 |
31.10 |
|
Sankhola 76 |
18615 |
13569 |
13019 |
34.33 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001,Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Remnants of the architecture and stone inscription of the Murarbandar Dargah Sharif.
Historical events Rajapur of this upazila was the capital of Tipra king Achaknarayan who was defeated in a battle with the army of Syed Nasiruddin, Commander of the Bengal Sultan Firoj Shah in 1304 AD.
Marks of War of Liberation Mass killing site 1 (Nalua Tea Garden); memorial monument 1.
Religious institutions Mosque 338, temple 29, tomb 5, most noted of which are the tombs of Syed Shah Gada Hasan (R) and Syed Sharful Hasan (R) of village Narapati.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 32.87%; male 37.79%, female 27.92%. Educational institutions: college 2, secondary school 27, primary school 110, kindergarten 1, madrasa 30. Noted educational institutions: Mirashi High School (1887), Rajar Bazar Government High School (1867), Dakkhina Charan Pilot High School (1928), Gazipur High School (1964), Agrani High School (1969), Ubahata Kudratia Dakhil Madrasa (1870), Sankhola Dakhil Madrasa (1928), Gabtala Dakhil Madrasa (1933).
Newspapers and periodicals Weekly Tarafbarta.
Cultural organisations Library 1, club 15, community centre 2, cinema hall 1, auditorium 1, literary association 2, playground 10.
Tourist spots Chandpur and Chandichhara Tea Garden.
Main sources of income Agriculture 54.71%, non-agricultural labourer 16.03%, commerce 8.04%, transport and communication 2.51%, service 3.61%, construction 0.85%, religious service 0.31%, rent and remittance 1.07% and others 12.87%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 48.04%, landless 51.96%; agricultural landowner: urban 55.78% and rural 47.81%.
Main crops Paddy, wheat, sugarcane, bean, potato, sesame, mustard, tea.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Linseed.
Main fruits Mango, black berry, banana, jackfruit, litchi, pineapple.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 25, dairy 40, poultry 52.
Communication facilities Pucca road 37 km, semi-pucca road 121 km; waterway 12 nautical miles.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, soari.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, blacksmith, weaving, potteries, wood work, bamboo work.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 23, most noted of which are Chunarughat Bazar, Chandpur Garden Bazar, Amu Road Bazar, Nalmukh Bazar and Haziganj Bazar.
Main exports Tea, paddy.
Access to electricity All the wards and unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 25.49% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Mineral resources' Glass sand in the hilly area.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 79.18%, pond 5.75%, tap 5.07% and others 10%.
Sanitation 19.97% (rural 18.65% and urban 63.15%) of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 59.27% (rural 60.05% and urban 33.60%) of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 20.76% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, union health and family welfare centre 1, family planning centre 10, maternity and child welfare centre 2, charitable hospital 1, satellite clinic 9, diagnostic centre 1, veterinary hospital 1.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are CARE, brac, asa. [Jayanta Singh Roy]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Chunarughat Upazila 2007.
