Magura Sadar Upazila
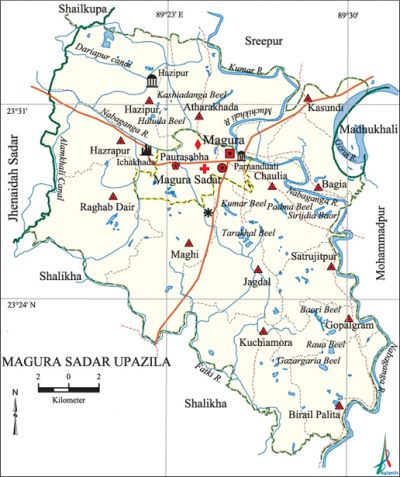
Magura Sadar Upazila (magura district ) area 406.5 sq km, located in between 23°17' and 23°34' north latitudes and in between 89°17' and 89°32' east longitudes. It is bounded by sreepur (magura) and shailkupa upazilas on the north, salikha upazila on the south, mohammadpur (Magura) and madhukhali upazilas on the east, jhenaidah sadar and Salikha upazilas on the west.
Population Total 331494; male 170369, female 161125; Muslim 269248, Hindu 61747, Buddhist 247, Christian 12 and others 240.
Water bodies Main rivers: Gorai, Nabaganga, Muchikhali, kumar, Fatki; Dariapur Canal, Alamkhali Canal, Sirijdia Baor and Tarakhal, Baori, Raua, Padma, Kumar, Kashiadanga, Gazar Garia and Hatuda beels are notable.
Administration Magura Thana was turned into an upazila in 1983.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| 1 | 13 | 222 | 236 | 86445 | 245049 | 815 | 59.3 | 40.8 |
| Municipality | ||||||||
| Area (sq km) | Ward | Mahalla | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | |||
| 47.3 | 9 | 61 | 86445 | 1828 | 59.3 | |||
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
| Area (sq km) | Mouza | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||||
| 14.35 | 61 | 18878 | 1315 | 54.64 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
| Atharakhada 21 | 9842 | 9429 | 8939 | 43.32 |
| Kasundi 61 | 3858 | 3250 | 3023 | 53.14 |
| Kuchiamora 67 | 8831 | 12519 | 11896 | 39.09 |
| Gopalgram 33 | 3840 | 5660 | 5650 | 39.70 |
| Chaulia 27 | 7784 | 11829 | 11362 | 39.35 |
| Jagdal 54 | 8680 | 10535 | 9900 | 33.62 |
| Bagia 25 | 4380 | 7789 | 7549 | 48.07 |
| Birail Palita 23 | 6821 | 9143 | 8748 | 44.39 |
| Maghi 74 | 9331 | 14007 | 13113 | 38.17 |
| Raghab Dair 88 | 9738 | 12425 | 11957 | 34.12 |
| Satrujitpur 94 | 4491 | 8382 | 7870 | 37.23 |
| Hazrapur 47 | 5793 | 9169 | 8754 | 42.40 |
| Hazipur 40 | 10139 | 11154 | 10997 | 49.13 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Neelkuthi (Ichakhada), Beparipara Jami Mosque (Parnanduali), tomb of Pir Mokarram Ali (Hazipur), Siddheshwari Math (Darimagura), Radhanagar Math (Ramnagar).
History of the War of Liberation Magura sadar was under Sector 8 during the war of liberation. The Pak army conducted mass killing and plundering in the upazila and set many houses on fire.
Marks of the War of Liberation Memorial monument 1 (adjacent to the Bishwa Road).
Religious institutions Mosque 250, temple 55, church 1, tomb 2, sacred place 3. Noted religious institutions: Magura Jami Mosque, Beparipara Jami Mosque (Parnanduali), Kalibari Mandir, tomb of Pir Mokarram Ali (Hazipur), ashram of Nangta Baba (Satdoha), Math and Mission at Hajratala, Siddheshwari Math (Darimagura), Radhanagar Math (Ramnagar).
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 45.8%; male 50.2%, female 41.1%. Educational institutions: college 5, technical college 1, secondary school 33, primary school 147, madrasa 2. Noted educational institutions: Government Hossain Shahid Suhrawardi College (1940), Magura Government Boys' High School (1854), Hazipur Secondary School (1914), Shatrujitpur Kaliprasanna Secondary School (1919).
Newspapers and periodicals Daily: Khedmat; weekly: Magura Barta, Grameen Bangla, Ganasangbad, Angikar; monthly: Nabaganga.
Cultural organisations Library 3, club 90, theatre group 4, jatra party 2, literary organisation 2, women organisation 3, shilpakala academy 1, cinema hall 2.
Main sources of income Agriculture 60.52%, non-agricultural labourer 3.37%, industry 0.96%, commerce 13.97%, transport and communication 4.03%, service 9.02%, construction 1.81%, religious service 0.14%, rent and remittance 0.45% and others 5.73%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 61.64%, landless 38.36%; agricultural landowner: urban 43.3% and rural 68.31%.
Main crops Paddy, jute, wheat, mustard, gram, masuri, sugarcane, vegetables.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Sweet potato, kaun, arahar.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, litchi, blackberry, banana, papaya, indian apple, guava, futi, water-melon.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 62, poultry 28, hatchery 7.Communication facilities 'Pucca road 170 km, semi-pucca road 90 km, mud road 850 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, bullock cart and buffalo cart.
Noted manufactories Textile mill, plastic pipe factory, lathe industry, Bidi factory, ice factory, soap factory, welding factory.
Cottage industries Blacksmith, potteries, weaving, bamboo and cane work.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 35, fairs 10, most noted of which are Magura Ekata Kacha Bazar Hat, Shatrujitpur Hat, Ichakhada Hat, Alokdia Hat, Katakhali Hat, Rathkhola Mela, Katayani Mela and Baishakhi Mela.
Main exports Jute, yarn, vegetables.
Access to electricity All the wards and unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 24.81% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 91.22%, pond 0.18%, tap 3.69% and others 4.91%.
Sanitation 26.49% (rural 17.86% and urban 50.23%) of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 55.72% (rural 60.78% and urban 41.78%) of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 17.79% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Zila Sadar hospital 1, upazila health centre 1, shishu hospital 1, eye hospital 1, diabetic hospital 1, maternity hospital 1, family welfare centre 13, satellite clinic 7.
Natural disasters Many people were victims of the cyclones of 1585, 1668, 1869, and 1909; these natural disasters also caused heavy damages to settlements, livestock and crops of the upazila.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are brac, asa, proshika, Swanirvar Bangladesh, Seba. [Ranjit Kumar Basu]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Magura Sadar Upazila 2007.
