Sapahar Upazila
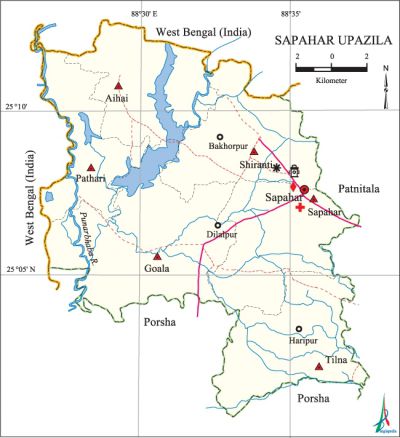
Sapahar Upazila (naogaon district) area 244.49 sq km, located in between 25°01' and 25°13' north latitudes and in between 88°26' and 88°38' east longitudes. It is bounded by west bengal state of India on the north, porsha upazila on the south, patnitala upazila on the east, West Bengal state of India on the west.
Population Total 143853; male 73974, female 69879; Muslim 133893, Hindu 6796, Buddhist 1007, Christian 31 and others 2126. Indigenous communities such as santal, oraon and Mahali belong to this upazila.
Water bodies Main river: punarbhaba.
Administration Sapahar Thana was formed in 1979 and it was turned into an upazila on 1 March 1985.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
|
- |
6 |
151 |
234 |
10675 |
133178 |
588 |
59.3 |
38.7 |
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Mouza |
Population |
Density (per sq km) |
Literacy rate (%) | ||||
|
8.39 |
4 |
10675 |
1272 |
59.31 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
|
Aihai 7 |
9393 |
9529 |
9234 |
36.08 |
|
Goala 39 |
14304 |
16436 |
15791 |
32.71 |
|
Tilna 94 |
9965 |
10431 |
9873 |
53.13 |
|
Pathari 63 |
7064 |
11050 |
10569 |
25.84 |
|
Shiranti 79 |
10006 |
12742 |
11919 |
40.88 |
|
Sapahar 71 |
9684 |
13786 |
12493 |
52.41 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
History of the War of Liberation Sapahar upazila was under Sector 7 during the war of liberation. On 14 August the freedom fighters killed 5 Pak soldiers and destroyed a jeep by dynamite explosion on the Hapania Road. In retaliation, the Pak army conducted indiscriminate mass killing at Hapania and the nearby villages. The Pak army conducted mass killing at village Pahari Pukur of Aihai union and at Hatidanga on the backyard of Sapahar Mohila College.
Marks of the War of Liberation Mass grave 1 (Hatidanga).
Religious institutions Mosque 225, temple 23, keyang 67, church 1. Noted religious institutions: Tilna Mosque, Alinagar Jami Mosque, Cremation Centre and Mandir on the bank of the Punarbhaba river.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 40.4%; male 43.6%, female 37%. Educational institutions: college 6, secondary school 38, primary school 114, kindergarten 3, computer training centre 1, madrasa 51. Noted educational institutions: Sapahar Government Degree College (1973), Sapahar Mohila College (1995), Kata Para ML High School (1929), Tegharia High School (1958), Tilna High School (1958), Sapahar Pilot High School (1962), Mirapara High School (1964), Kochkurulia High School (1964), Chalk Gopal High School (1964), Sapahar Government Girls' High School (1973), Pathari Fazil Madrasa (1961).
Newspapers and periodicals Irregular: Yuger Bani.
Cultural organisations Library 3, club 55, cinema hall 1, theatre stage 1, theatre group 4, playground 30.
Main sources of income Agriculture 79.03%, non-agricultural labourer 2.23%, commerce 7.46%, transport and communication 1.32%, service 3.76%, construction 0.37%, religious service 0.10%, rent and remittance 0.07% and others 5.66%.
Main crops Paddy, wheat, mustard, vegetables.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Aus paddy, sesame, linseed, arahar.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, banana, papaya, watermelon.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 11, dairy 8, poultry 32.
Communication facilities Pucca road 65 km, semi-pucca road 30 km, mud road 265 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, horse carriage.
Noted manufactories Rice mill, flour mill, ice factory, welding factory.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, blacksmith, potteries, wood work, weaving, bamboo work, nakshi kantha, nakshi pakha.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 23, fairs 2, most noted of which are Sapahar Hat, Dighi Para Hat, Mirapara Hat, Pora Madhail Hat, Nischintapur Bazar, Shiranti Bazar, Pathari Bazar, Tilna Bazar and Gopalpur Bazar.
Main exports Paddy, wheat, mustard, watermelon.
Access to electricity All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 7.18% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 69.44%, tap 0.52%, pond 1.21% and others 28.83%.
Sanitation 10.85% (rural 8.54% and urban 37.85%) of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 19.25% (rural 19.33% and urban 18.26%) of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 69.90% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, union health and family welfare centre 9, clinic 1, community clinic 17.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are brac, proshika, asa, Ujjiban, caritas. [Md. Mukhlesur Rahman]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Sapahar Upazila 2007.
