Sylhet Sadar Upazila
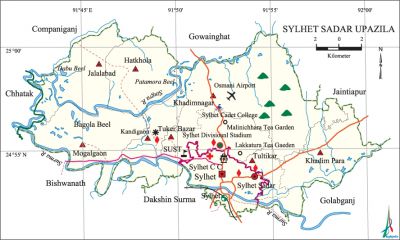
Sylhet Sadar Upazila (sylhet district) area 323.17 sq km, located in between 24°52' and 25°02' north latitudes and in between 91°01'and 91°40' east longitudes. It is bounded by companiganj, gowainghat and jaintiapur upazilas on the north, dakshin surma upazila on the south, Jaintiapur and golapganj upazilas on the east, chhatak and bishwanath upazilas on the west.
Population Total 493784; male 266701, female 227083; Muslim 441539, Hindu 50919, Buddhist 717, Christian 239 and others 370. Indigenous communities such as khasia and manipuri belong to this upazila.
Water bodies Main rivers: surma, kushiyara, Singra; Dabu Beel, Bagola Beel and Patamora Beel are notable.
Administration Sylhet Sadar Thana was turned into an upazila in 1984.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
|
1 |
8 |
84 |
372 |
316311 |
230587 |
1528 |
67.88 |
45.13 |
| City Corporation | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Ward |
Mahalla |
Population |
Density (per sq km) |
Literacy rate (%) | |||
|
21.09 |
27 |
207 |
263197 |
12480 |
69.73 | |||
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Mouza |
Population |
Density (per sq km) |
Literacy rate (%) | ||||
|
31.14 |
14 |
53114 |
951 |
66.00 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
|
Kandigaon 38 |
8672 |
16642 |
16242 |
40.14 |
|
Khadimnagar 40 |
18844 |
20158 |
18663 |
39.74 |
|
Khadim Para 42 |
11303 |
27518 |
25003 |
56.95 |
|
Jalalabad 34 |
8473 |
7107 |
6911 |
34.28 |
|
Tuker Bazar 90 |
8342 |
19403 |
16646 |
49.79 |
|
Tultikar 95 |
3668 |
4404 |
3508 |
63.77 |
|
Mogalgaon 55 |
7568 |
11134 |
10991 |
36.99 |
|
Hatkhola 32 |
8649 |
11365 |
11430 |
39.42 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Stone inscription of the tomb of shah jalal (r), Ghardoar Nawabi Mosque, statue made of black basalt at Bishwamvar Akhra, stone inscription of Shahi Eidgah, Kreen Bridge.
History of the War of Liberation A serious encounter between the freedom fighters and the Pak army was held on 4 April 1971 at the hospital area of the upazila in which a number of Pak soldiers and freedom fighters were killed. On 5 April the freedom fighters attacked the Sylhet Airport and exploded bomb causing heavy damages to the airport. To control the situation most of the Pak army rushed to the airport area. Taking advantage, the freedom fighters entered into the Sylhet Jail and liberated about 2500 people including the freedom fighters. On 19' April the freedom fighters launched an attack on the Airport again. During the war of liberation more than one hundred freedom fighters were killed in various encounters with the Pak army including at Laltila, Ureatila, Malinichhara Tea Garden, Tultikar, Zindabazar Police Line, Jalalabad etc. Sylhet Town was liberated on 16 December.
Marks of the War of Liberation Mass killing site 6 (Sylhet Cadet College, Civil Surgeon's Bungalow, Laltila, Ureatila, Khadimnagar, Sheikh Burhanuddin Road); Mass grave 6 (Zindabazar Police Line, Malnichhara Tea Garden, Cadet College, Tultikar); memorial monument 6; sculpture 1 (memorial sculpture at Jalalabad Cantonment).
Religious institutions Mosque 375, temple 12, church 2, Math 2, tomb 6. Noted religious institutions: Sheikh Sunaullah Mosque, Nawabi Mosque, Dargah Mosque, Kudrat Ullah Mosque, Shah Paran Mosque, Abu Turab Mosque, tomb of Hazrat Shah Jalal (R), tomb of Hazrat shah paran (r), tomb of Garam Dewan, tomb of Panch Pir, tomb of Zindah Pir, Shiva Mandir of Gotatik, Kalighat Kali Mandir, Satir Pithasthan, Jainpur Pithasthan, Sath Sanga Vihara, Ramkrisna Mission and Math, Presbyterian Church (1897), Church at Nayasarak.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 59.14%; male 63.09%, female 54.61%. Educational institutions: university 5, medical college 4, technical college 3, college 7, secondary school 44, primary school 115, community school 6, kindergarten 80, madrasa 30. Noted educational institutions: shahjalal university of science and technology (1987), Sylhet Agricultural University, Darul Ihsan University, MAG Osmani Medical College (1975), Sylhet Engineering College, Jalalabad Public School and College, MC college (1889), Sylhet Sanskrit College (1902), Sylhet Government Pilot High School (1836), Raja Jimi High School (1886), Agragami Government Girls' High School (1903), Model High School (1932), Government Madan Mohan College (1940), The Aided High School (1942), Kishori Mohan Girls' School (1944), Hazrat Shah Jajal (R) High School, Hazrat Shah Paran (R) High School, Sylhet' Government Alia Madrasa (1948).
Newspapers and periodicals Daily: Sylheter Dak, Sabuj Sylhet, Sylhet Sanglap, Manchitra, Yugveri, Sylhet Bani, Alokito Sylhet, Jalalabad; defunct: Shrihatta Prakash (1875), Paridarshak (1875-80), Srihattamihir (1889), Shrihattabasi (1895), Janashakti (1920), Jugbani (1925), Gyanannesan (1931), Jagaran (1938), Al Jalal (1941), Sylhet Samachar (1977), Sylhet Kantha (1981), Weekly Jalalabad (1982), Daily Jalalabadi (1984), Daily Sudin (1992), Ajker Sylhet (1992), Ajker Vishwa Sangbad (1992).
Tourist spots Tomb of Shah Jajal (R), tomb of Hazrat Shah Paran (R), Gour Gobinda Fort, Malnichhara Tea Garden, MAG Osmani International Airport, Osmani Museum, Museum of Rajars', Parjatan Motel.
Cultural organisations Library 3, museum 3, cinema hall 8, auditorium 5, theatre stage 3, theatre group 10, women organisation 3, literary organisation 6, playground 4.
Main sources of income Agriculture 16.44%, non-agricultural labourer 5.31%, industry 1.61%, commerce 24.45%, transport and communication 5.91%, service 17.14%, construction 3.00%, religious service 0.32%, rent and remittance 6.38% and others 19.44%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 36.30%, landless 63.70%.
Main crops Paddy, tea, potato, vegetables, onion, garlic, betel leaf.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Sesame, linseed, mustard, kaun, black pepper.
Main fruits Water melon, pomegranate, orange, wood-apple.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 50, dairy 5, poultry 100, hatchery 15.
Communication facilities Pucca road 201.41 km, semi-pucca road 8 km, mud road 650 km; railway 49.07 km;' culvert 750, bridge 15; airport 1.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, horse carriage, bullock cart.
Noted manufactories Rice mill, flour mill, ice factory, textile mill, bidi factory.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, blacksmith, weaving, potteries, wood work, bamboo and cane work.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 32, fairs 6, most noted of which are Kazir Bazar, Jalalabad Bazar, Hatkhola Bazar, Kalighat Bazar, Lal Bazar, Rikabi Bazar, Mira Bazar, Zinda Bazar, Shibganj Bazar, Shah Paran Bazar, Khadimnagar Bazar, Salutikar Bazar, Islampur Manipuri Rajbari Mela, Rathjatra Mela, Chaitra Mela, Chalibandar Charak Mela and Maharram Mela (Shahi Eidgah).
Main exports Natural gas, tea, betel leaf, orange, dried fish, Manipuri cotton fabrics, bamboo and cane furniture, shital pati.
Access to electricity All the wards and unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 62.30% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Natural resources Natural gas.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 72.11%, tap 16.08%, pond 7.67% and others 4.14%.
Sanitation 63.98% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 28.88% of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 7.14% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Hospital 5, health and family welfare centre 7, community clinic 20, clinic 22, family planning centre 5.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are brac, CARE, asa, Save the Children. [Md. Farruk Ahmed Chowdhury]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Field report of Sylhet Sadar Upazila 2010.
