Faridganj Upazila
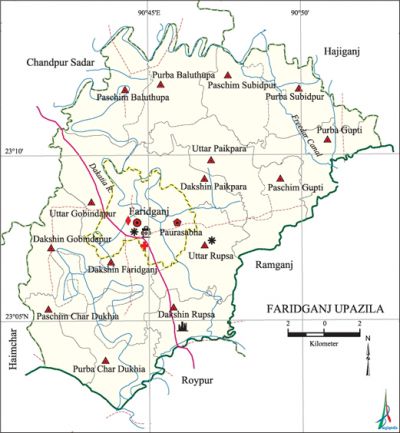
Faridganj Upazila (chandpur district) area 231.54 sq km, located in between 23°03' and 23°14' north latitudes and in between 90°41' and 90°53' east longitudes. It is bounded by chandpur sadar and hajiganj upazilas on the north, raipur upazila on the south, ramganj upazila on the east, haimchar and Chandpur Sadar upazilas on the west.
Population Total 374760; male 182124, female 192636; Muslim 356480, Hindu 18164, Buddhist 66 and others 50.
Water bodies dakatia river and Guptir Beel are notable.
Administration Faridganj Thana, now an upazila, was formed on 7 October 1918.'
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
|
1 |
15 |
178 |
175 |
6824 |
367936 |
1619 |
62.46 |
53.64 |
| Municipality | ||||||||
|
Area |
Ward |
Mahalla |
Population |
Density |
Literacy rate (%) | |||
|
15.75 |
- |
- |
26095 |
1657 |
58.56 | |||
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Mouza |
Population |
Density (per sq km) |
Literacy rate (%) | ||||
|
2.47 |
1 |
6824 |
2763 |
62.46 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
|
Uttar Gobindapur 41 |
3828 |
13846 |
14310 |
48.31 |
|
Uttar Paikpara 65 |
3933 |
11339 |
12369 |
57.23 |
|
Uttar Rupsa 77 |
4004 |
13271 |
13961 |
52.42 |
|
Dakshin Gobindapur 47 |
2894 |
12246 |
12752 |
48.13 |
|
Dakshin Paikpara 71 |
3115 |
10814 |
11785 |
56.81 |
|
Dakshin Faridganj 35 |
3986 |
10335 |
11133 |
49.09 |
|
Dakshin Rupsa 83 |
2858 |
9462 |
10378 |
56.24 |
|
Paschim Gupti 59 |
2669 |
9586 |
10385 |
59.01 |
|
Purba Gupti 53 |
3571 |
10055 |
10442 |
55.86 |
|
Paschim Char Dukhia 23 |
2778 |
11088 |
11082 |
47.25 |
|
Purba Char Dukhia 17 |
4041 |
11820 |
12615 |
50.53 |
|
Paschim Baluthupa 11 |
4107 |
11323 |
11819 |
56.41 |
|
Purba Baluthupa 05 |
3969 |
12292 |
13593 |
56.53 |
|
Paschim Subidpur 95 |
3560 |
10998 |
11168 |
55.63 |
|
Purba Subidpur 89 |
3965 |
10714 |
11684 |
54.87 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Neelkuthi (indigo factory) at Sahebganj, Math at Lohagara, Rupsa Zamindar Bari, Rupsa Mosque.
History of the War of Liberation During the War of Liberation in 1971, 64 freedom fighters and a number of local people were killed in encounters with the Pak army. Faridganj was liberated on 14 December.
Marks of the War of Liberation Mass grave 1, memorial monument 1.
Religious institutions Mosque 575, temple 11, church 1, math 1.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 53.8%; male 54.7%, female 53%. Educational institutions: college 8, secondary school 47, primary school 252, community school 13, madrasa 237. Noted educational institutions: Faridganj Degree College (1970), Chandra Imam Ali College (1994), Gallak Adarsha College (1994), Gredakalindia Hajera Hasmath Degree College (1995), Baragaon High School (1899), Chandra Imam Ali High School (1918), Grehakalindia High School (1926), Paikpara U.G High School (1913), Basara High School (1926), Rupsa Ahmadia High School (1913), Kaonia Shaheed Habibullah High School (1926), Hansa Fazil Madrasa (1902).
Newspapers and periodicals Faridganj Barta, Palli Kahini.
Cultural organisations Library 4, club 48, cinema hall 1, women's organisation 1.
Main sources of income Agriculture 42.90%, non-agricultural labourer 2.64%, industry 0.86%, commerce 15.24%, transport and communication 2.63%, service 13.80%, construction 3.50%, religious service 0.43%, rent and remittance 5.39% and others 12.61%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 60.78%, landless 39.22%; agricultural landowner: urban 33.63% and rural 61.30%.
Main crops Paddy, wheat, potato, sugarcane, betel leaf.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Sesame, linseed, kaun, mustard, khesari pulse.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, coconut, banana, betel nut.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 19, dairy 71, poultry 134.
Communication facilities Pucca road 125 km, semi-pucca road 40 km, mud road 325 km; waterway 19 nautical miles.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, bullock cart, horse carriage.
Noted manufactories Rice mill, ice factory, ice-cream factory, welding factory.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, blacksmith, potteries, embroidery, wood work, bamboo work.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 45, fairs 6, most noted of which are Rupsa Hat, Gallak Hat, Gredakalindia Hat, Chandra Hat and Baishakhi Mela.
Main exports Sugarcane, betel leaf, potato.
Access to electricity All the wards and unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 24.98% (urban 62.87% and rural 24.25%) of the dwellings have access to electricity.'
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 77.44%, tap 0.45%, pond 17.43% and others 4.68%. The presence of arsenic has been detected in the shallow tube-well water of the upazila.
Sanitation 53.57% (urban 81.87% and rural 53.03%) of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 34.59% (urban 10.60% and rural 35.05%) of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 11.84% (urban 7.53% and rural 11.92%) of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, family welfare centre 11, satellite clinic 1, maternity centre 1.
NGO activities brac, asa, proshika, BRDB, Mahila Unnayan Sangstha. [Musammat Rahima Begum]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Faridganj Upazila 2007.
