Maheshkhali Upazila
Maheshkhali Upazila (cox’s Bazar district) area 362.18 sq km, located in between 21°28' and 21°46' north latitudes and in between 91°51' and 91°59' east longitudes. It is bounded by chakaria upazila on the north, cox’s bazar sadar upazila and bay of bengal on the south, Chakaria and Cox's Bazar Sadar upazilas on the east, kutubdia upazila and Bay of Bengal on the west.
Population Total 256546; male 135222, female 121324; Muslim 238159, Hindu 15781, Buddhist 34, Christian 2557 and others 15.
Water bodies Main rivers: Kohalia; Maheshkhali Channel, Boddar Canal, Noachi Canal, Koria Canal are notable.
'Administration Maheshkhali Thana was turned into an upazila on 15 December 1983.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
|
1 |
12 |
150 |
196 |
23100 |
273148 |
731 |
50.5 |
43.1 |
| Municipality | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Ward |
Mahalla |
Population |
Density (per sq km) |
Literacy rate (%) | |||
|
21.34 |
9 |
16 |
23100 |
2014 |
50.5 | |||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
|
Azampur10 |
7935 |
10691 |
9934 |
45.51 |
|
S.K.B. 83 |
5639 |
7989 |
7506 |
50.67 |
|
Kazirber 29 |
8756 |
15135 |
14498 |
36.99 |
|
Natima 53 |
9281 |
11713 |
11049 |
43.06 |
|
Nepa 59 |
8486 |
13240 |
12567 |
41.70 |
|
Pantha Para 65 |
8485 |
8736 |
8336 |
44.32 |
|
Fatehpur 17 |
7404 |
11096 |
10478 |
48.57 |
|
Banshbaria 11 |
9159 |
13867 |
13255 |
39.57 |
|
Manderbari 35 |
7250 |
13016 |
12219 |
50.67 |
|
Jadabpur 23 |
9664 |
12801 |
12439 |
42.77 |
|
Shyamkur 77 |
8310 |
11950 |
11273 |
38.56 |
|
Swaruppur 89 |
8025 |
9955 |
9405 |
38.38 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
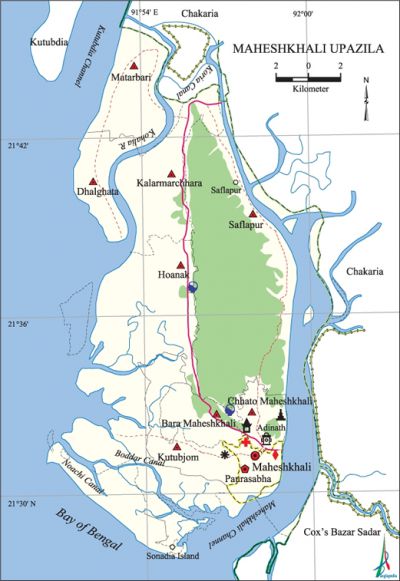
Archaeological heritage and relics adinath temple (Mainak Hill, Gorakghata Union).
Historical events As evidenced by the Portuguese traveller Caesar Frederick and corroborated by the modern historians the island of Maheshkhali had its origin consequent upon its separation from the mainland by severe cyclone and tidal bore of 1559.
Religious institutions Mosque 210, temple 26, buddhist keyang 6.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 22.5%; male 25.5%, female 19.3%. Educational institutions: college 10, secondary school 33, primary school 70, kindergarten 12, madrasa 33. Noted educational institutions: Maheshkhali College (1985), Maheshkhali Government Vernacular School (1923), Maheshkhali Model High School (1946).
Newspapers and periodicals Maheshkhali Barta, Alor Dwip.
Cultural organisations Library 1, club 13.
Amusement centres or tourists spots Adinath Temple, Mainak Hill, Sonadia Island, keyang of the rakhain.
Main sources of income Agriculture 61.92%, non-agricultural labourer 7.26%, commerce 15.46%, transport and communication 1.49%, service 2.74%, construction 0.56%, religious service 0.20%, rent and remittance 0.45% and others 9.92%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 33.23%, landless 66.77%; agricultural landowner: urban 20.93% and rural 33.94%.'
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Pearl production.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, litchi, banana, papaya, coconut.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries This upazila has a number of fisheries, dairies and poultries.
Communication facilities Pucca road 91 km, semi-pucca road 15 km, mud road 191 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, horse carriage, bullock cart.
Noted manufactories Salt industry, fish processing industry, flour mill, ice mill.
Cottage industries Weaving, potteries, handicrafts.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 15, fair 1, most noted of which are Gorakghata Bazar, Bara Maheshkhali Bazar, Kalarmarchhara Bazar, Time Bazar and Adinath Mela.
Main exports Salt, shrimp, sea-fish, dry fish.
Access to electricity All the wards and unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 13.34% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 91.84%, tap 0.46%, pond 1.09% and others 6.61%.
Sanitation 25.55% (rural 23.59% and urban 59.16%) of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 56.21% (rural 57.48% and urban 28.24%) of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 18.24% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, satellite clinic 1, union health and family planning centre 6, pathology' 4.
Natural disasters Many people were victims of the cyclone and tidal bore of 29 April 1991. It also caused heavy damages to settlements, livestock and other crops of the upazila.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are caritas, Christian Commission Development in Bangladesh, Prism Bangladesh. [Mohammad Jasim Uddin]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Maheshkhali Upazila 2007.
