Tahirpur Upazila
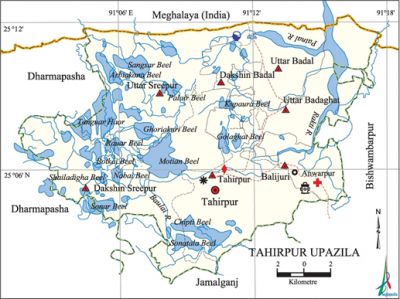
Tahirpur Upazila (sunamganj district) area 313.70 sq km, located in between 25°01' and 25°12' north latitudes and in between 91°02' and 91°19' east longitudes. It is bounded by Meghalaya state of India on the north, jamalganj and dharmapasha upazilas on the south, bishwambarpur upazila on the east, Dharmapasha upazila on the west.
Population Total 155188; male 80537, female 74651; Muslim 140111, Hindu 14362, Buddhist 578, Christian 23 and others 114. Indigenous communities such as garo and hajong belong to this upazila.
Water bodies Main rivers: Baulai, Patnal, Rakti; Tanguar Haor,' Matian Beel, Sangsar Beel, Arbiakona Beel, Rauar Beel, Sonar Beel, Chipti Beel, Sonatala Beel, Palair Beel, Ghoriakuri Beel, Botkai Beel, Shailadigha Beel, Nabai Beel, Kupaura Beel, Golaghat Beel are notable.
Administration Tahirpur Thana, now an upazila, was formed in 1924.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
|
- |
7 |
136 |
244 |
7395 |
147793 |
495 |
42.0 |
30.6 |
| Upazila Town | |||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Mouza |
Population |
Density (per sq km) |
Literacy rate (%) | |
|
4.13 |
1 |
7395 |
1791 |
42.02 | |
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
|
Uttar Badal 82 |
8405 |
13035 |
12479 |
20.93 |
|
Uttar Badaghat 71 |
8799 |
16924 |
16530 |
29.76 |
|
Uttar Sreepur 92 |
23424 |
17761 |
15696 |
34.05 |
|
Tahirpur 64 |
12962 |
7964 |
7336 |
33.81 |
|
Dakshin Badal 43 |
4269 |
8949 |
7878 |
33.60 |
|
Dakshin Sreepur 33 |
14597 |
8651 |
7954 |
34.33 |
|
Balijuri 10 |
3953 |
7253 |
6778 |
36.24 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Remnants of the residence of Raja Bijoy Singh (16th century).
Historical events During the war of liberation in 1971, a number of refugee camps were established on the foot of the Khasia Jainta hills near Tahirpur. In 1997-98 Bhasan Pani Movement was held in Tahirpur in which 10 peasants were killed and many were arrested and were kept confined.
Religious institutions Mosque 233, temple 45, church 1, tomb 3, sacred place 1.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 31.2%; male 36.2%, female 25.9%. Noted educational institutions: Zainal Abedin College (1992), Badaghat College (1994), Tahirpur Government High School (1950), Tahirpur Girls' High School (1988), Badaghat High School (1962), Takerghat Chunapathar Khani Prokalpa High School (1966), Janata High School (1989), Balijuri High School (1965), Tahirpur Hifzul Ulam Senior Madrasa (1973), Rahmania Senior Madrasa (1973).
Cultural organisations Library 1, club 10, women organisation 1, playground 3.
Tourist spots Tanguar Haor, Janmadham (birth place) of Sree Sree Adaita Prabhu, Pana Tirtha and Barek Tila.
Main sources of income Agriculture 68.05%, non-agricultural labourer 7.53%, industry 0.35%, commerce 11.56%, transport and communication 1.07%, service 2.30%, construction 0.57%, religious service 0.32%, rent and remittance 0.22% and others 8.03%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 59.34%, landless 40.66%; agricultural landowner: urban 60.84% and rural 59.27%.
Main crops Paddy, nut, wheat, mustard.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Tobacco, kaun.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, banana, papaya, lemon, watermelon.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 10, dairy 20, poultry 70.
Communication facilities Pucca road 15 km, mud road 201 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, bullock cart.
Cottage industries Weaving, bamboo work, cane work.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 20, fairs 2, most noted of which are Badaghat Bazar, Tahirpur Bazar, Balijuri Bazar, Anwarpur Bazar, Panatirtha Baruni Mela at Rajargaon and Shah Arefin Mela at Laurergarh.
Main exports Paddy, fish, lime stone.
Access to electricity All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 3.93% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Natural resources Lime stone, sand and coal.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 81.74%, tap 1%, pond 4.54% and others 12.72%.
Sanitation 11.23% (rural 9.90% and urban 38.69%) of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 77.08% (rural 77.87% and urban 60.84%) of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 11.69% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health centre 1, family planning centre 7, satellite clinic 1.
Natural disasters The floods of 1974, 1988 and 1998 caused heavy damages to cattle and other properties of the upazila.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are brac, asa. [Jayanta Singh Roy]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Tahirpur Upazila 2007.
