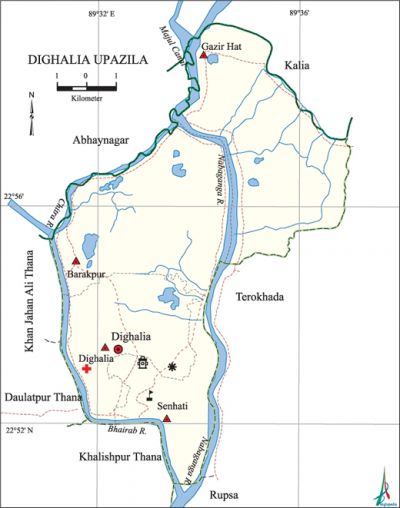
Dighalia Upazila
Dighalia Upazila (khulna district) area 77.16 sq km, located in between 22°50' and 22°59' north latitudes and in between 89°33' and 89°40' east longitudes. It is bounded by abhaynagar and kalia upazilas on the north, khalishpur thana and rupsa upazila on the south, terokhada upazila on the east, daulatpur and khan jahan ali thanas and Abhaynagar upazila on the west.
Population Total 115585; male 59220, female 56365; Muslim 97860, Hindu 17210, Christian 508 and others 7.
Water bodies Main rivers: bhairab, chitra, nabaganga; Majul Canal, Kachua Beel, Nandan Pratap Beel, Hazir Hat Beel and Thakurjhi Dighi are notable.
Administration Dighalia Thana was turned into an upazila on 12 January 1987.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| - | 4 | 29 | 43 | 4945 | 110640 | 1498 | - | 54.3 |
| Upazila Town | ||||
| Area (sq km) | Mouza | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) |
| 4.01 | - | 4945 | 1233 | - |
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
| Gazir Hat 66 | 6512 | 9877 | 9556 | 46.8 |
| Dighalia 57 | 3835 | 14854 | 14664 | 59.5 |
| Barakpur 17 | 6083 | 11631 | 11276 | 54.1 |
| Senhati 85 | 2639 | 22858 | 20869 | 54.1 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2011,Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Kali Mandir (Senhati Shiva Bari), Basu Deva Mandir, Khan Jahan Ali Dighi at Panihati.
War of Liberation During the war of liberation in 1971 the Pak army carried out genocide, set fire on houses in many villages and looted them. Freedom fighters had a number of encounters with Pak army in the upazila and prominent among them was the one at a place between Gazirhat and Piroli Bazaar. A number of freedom fighters were martyred in the encounters.
For details: See দিগলিয়া উপজেলা, বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation Bangla Version), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ৪।
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 54.3%; male 56.6%, female 51.9%. Educational institutions: college 2, secondary school 21, primary school 43, madrasa 1. Noted educational institutions: Dighalia MA Majid College, Senhati Secondary School (1877), Lakhahati Secondary School (1969), Radha Madhabpur Government Primary School (1916).
Cultural organisations Club 10, cinema hall 1, community centre 4.
Main sources of income Agriculture 26.81%, non-agricultural labourer 5.85%, industry 5.28%, commerce 13.37%, transport and communication 2.62%, service 34.02%, construction 1.07%, religious service 0.26%, rent and remittance 0.54% and others 10.54%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 47.24%, landless 52.76%.
Main crops Paddy, wheat, sesame, mustard, betel leaf, vegetables.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Sugarcane, jute.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, litchi, coconut, banana, papaya, wood-apple, sapodilla, star-apple, blackberry.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries This upazila has a number of fisheries, dairies, poultries and hatcheries.
Communication facilities Pucca road 112 km, semi-pucca road 72 km, mud road 111 km; waterway 8 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, bullock cart.
Noted manufactories Jute mill, welding factory.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, potteries, blacksmith, embroidery, bamboo and wood work.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 16, most noted of which are Senhati, Batibhita, Lakhahati bazars and Kolar Hat, Gazir Hat, Majhirganti Hat and Kali Puja, Baishakhi and Eid melas.
Main exports Betel leaf, banana, papaya, vegetables.
Access to electricity All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 63.1% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 97.8%, tap 1.4% and others 0.8%.
Sanitation 92.7% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 6.3% of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 1.0% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health centre 1, satellite clinic 3, union health and family centre 7, clinic 1.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are' brac, asa, CARE, Nabolok, Prodipan. [Md Mamun Reza]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Dighalia Upazila 2007.
