Bhuapur Upazila: Difference between revisions
(Content Updated.) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
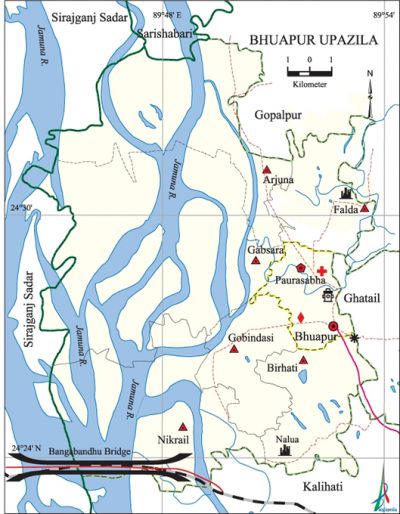
'''Bhuapur Upazila''' ([[Tangail District|tangail district]]) area | '''Bhuapur Upazila''' ([[Tangail District|tangail district]]) area 225.00 sq km, located in between 24°23' and 24'°35' north latitudes and in between 89°44' and 89°54' east longitudes. It is bounded by [[Gopalpur Upazila|gopalpur]] and [[Sarishabari Upazila|sarishabari]] upazilas on the north, [[Kalihati Upazila|kalihati]] upazilas on the south, Kalihati, [[Ghatail Upazila|ghatail]] and Gopalpur upazilas on the east, Jamuna river and [[Sirajganj Sadar Upazila|sirajganj sadar]] upazila on the west. | ||
''Population'' Total | ''Population'' Total 189913; male 92230, female 97683; Muslim 183748, Hindu 6146, Buddhist 2, Christian 4 and others 13. | ||
''Water bodies'' [[Jamuna River|jamuna]] river and Bhuapur beel are notable. | ''Water bodies'' [[Jamuna River|jamuna]] river and Bhuapur beel are notable. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| Urban || Rural || | Urban || Rural | | Urban || Rural || | Urban || Rural | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 1 || 6 || 93 || 128 || 28708 || 161205 || 844 || 59.0 || 41.0 | ||
1 | |||
| | |||
6 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
{| class="table table-bordered table-hover" | {| class="table table-bordered table-hover" | ||
| Line 57: | Line 40: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 13.69 || 9 || 21 || 28708 || 2097 || 59.0 | ||
13. | |||
| | |||
9 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
{| class="table table-bordered table-hover" | {| class="table table-bordered table-hover" | ||
| Line 80: | Line 49: | ||
| Male || Female | | Male || Female | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Arjuna 13 || 9901 || 12689 || 14104 || 41.1 | ||
Arjuna 13 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Aloa 27 || 4835 || 13301 || 14199 || 42.9 | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Gabsara 54 || 15924 || 12076 || 14602 || 27.3 | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Gobindasi 67 || 4347 || 16435 || 17004 || 46.4 | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Nikrail 81 || 10267 || 13103 || 12638 || 42.3 | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Falda 40 || 4792 || 10504 || 10993 || 46.1 | ||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
''Source'' Bangladesh Population Census | ''Source'' Bangladesh Population Census 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics. | ||
[[Image:BhuapurUpazila.jpg|thumb|400px]] | [[Image:BhuapurUpazila.jpg|thumb|400px]] | ||
'' | ''War of Liberation'' The Sarbadalio Sangram Parishad (the all party resistance Council) hoisted the flag of Bangladesh in a meeting held on 28 March 1971 at the foot of the Bhuapur College Shahid Minar. On 11 August the freedom fighters challenged a Pakistani river vessel carrying huge amount of arms and ammunitions at Sirajkandi and captured it. The freedom fighters later burnt the vessel. On 17 November the Pak army brutally killed 32 innocent persons at village Chhabisha of this upazila; they also set 350 houses on fire. There is a mass grave at Palsa School playground and a memorial sculpture has been established at the Ibrahim Kha College premises. | ||
'' | For details: see ভূঞাপুর উপজেলা, ''বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ'' (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ৭। | ||
''Religious institutions'' Mosque 135, temple 7. Noted religious institutions: Kismat Moria Mosque, Falda Jami Mosque, Kalidaha temple. | ''Religious institutions'' Mosque 135, temple 7. Noted religious institutions: Kismat Moria Mosque, Falda Jami Mosque, Kalidaha temple. | ||
''Literacy rate and educational institutions'' Average literacy | ''Literacy rate and educational institutions'' Average literacy 43.8%; male 46.6%, female 41.2%. Educational institutions: college 5, secondary school 27, primary school 104, madrasa 21. Noted educational institutions: Ibrahim Kha College (1948), Shamsher Fakir College (1986), Palashia Rani Dinomoni High School (1918), Falda Ramsundar Union High School (1925), Gobindasi High School (1930), Bhuapur Pilot High School (1941), Bhuapur Pilot Girls High School (1941), Bhuapur Fazil Madrasa (1976). | ||
''Cultural organisations'' Club 1, cinema hall 2, library 5,' theatre group 6, literary society 2, cultural organisation 4. | ''Cultural organisations'' Club 1, cinema hall 2, library 5,' theatre group 6, literary society 2, cultural organisation 4. | ||
| Line 197: | Line 88: | ||
''Fisheries, dairies and poultries'' Fishery 20, dairy 15 and Poultry 300. | ''Fisheries, dairies and poultries'' Fishery 20, dairy 15 and Poultry 300. | ||
''Communication facilities'' Roads: pucca | ''Communication facilities'' Roads: pucca road 77.42 km, Semi-pucca road 7.39 km, mud road 313.6 km; railway 12 km, waterway 15 km. Bridge 26. | ||
''Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport'' Bullock cart, 'horse carriage, palanquin, dhuli. | ''Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport'' Bullock cart, 'horse carriage, palanquin, dhuli. | ||
| Line 209: | Line 100: | ||
''Main exports'' Jute, leather, potato, vegetables, mustard. | ''Main exports'' Jute, leather, potato, vegetables, mustard. | ||
''Access to electricity'' All the unions of this upazila are under rural electrification net-work; however, | ''Access to electricity'' All the unions of this upazila are under rural electrification net-work; however, 47.8% dwelling households have access to electricity. | ||
''Sources of drinking water'' Tube-well | ''Sources of drinking water'' Tube-well 97.4%, tap 0.2 % and others 2.4%. | ||
''Sanitation'' | ''Sanitation'' 59.3% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 36.5% of dwelling houses use non-sanitary latrines; 4.2% of households do not have latrine facilities. | ||
''Health centres'' Upazila health complex 1, family planning centre 7, satellite clinic 2, village health centre 14, clinic 3. | ''Health centres'' Upazila health complex 1, family planning centre 7, satellite clinic 2, village health centre 14, clinic 3. | ||
| Line 219: | Line 110: | ||
''NGO activities'' [[BRAC|brac]], [[ASA|asa]], Serve, [[Caritas|caritas]], Barendra, SRC, Mukh. [Md Kaiser] | ''NGO activities'' [[BRAC|brac]], [[ASA|asa]], Serve, [[Caritas|caritas]], Barendra, SRC, Mukh. [Md Kaiser] | ||
'''References''' Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Bhuapur Upazila 2007. | '''References''' Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Bhuapur Upazila 2007. | ||
[[Category:Upazilas of Bangladesh]] | [[Category:Upazilas of Bangladesh]] | ||
Latest revision as of 10:51, 27 October 2023
Bhuapur Upazila (tangail district) area 225.00 sq km, located in between 24°23' and 24'°35' north latitudes and in between 89°44' and 89°54' east longitudes. It is bounded by gopalpur and sarishabari upazilas on the north, kalihati upazilas on the south, Kalihati, ghatail and Gopalpur upazilas on the east, Jamuna river and sirajganj sadar upazila on the west.
Population Total 189913; male 92230, female 97683; Muslim 183748, Hindu 6146, Buddhist 2, Christian 4 and others 13.
Water bodies jamuna river and Bhuapur beel are notable.
Administration Bhuapur Thana was formed in 1974 and it was turned into an upazila on 24 March 1983.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| 1 | 6 | 93 | 128 | 28708 | 161205 | 844 | 59.0 | 41.0 |
| Municipality | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Ward |
Mahalla |
Population |
Density (per sq km) |
Literacy rate (%) | |||
| 13.69 | 9 | 21 | 28708 | 2097 | 59.0 | |||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Papulation | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
| Arjuna 13 | 9901 | 12689 | 14104 | 41.1 |
| Aloa 27 | 4835 | 13301 | 14199 | 42.9 |
| Gabsara 54 | 15924 | 12076 | 14602 | 27.3 |
| Gobindasi 67 | 4347 | 16435 | 17004 | 46.4 |
| Nikrail 81 | 10267 | 13103 | 12638 | 42.3 |
| Falda 40 | 4792 | 10504 | 10993 | 46.1 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
War of Liberation The Sarbadalio Sangram Parishad (the all party resistance Council) hoisted the flag of Bangladesh in a meeting held on 28 March 1971 at the foot of the Bhuapur College Shahid Minar. On 11 August the freedom fighters challenged a Pakistani river vessel carrying huge amount of arms and ammunitions at Sirajkandi and captured it. The freedom fighters later burnt the vessel. On 17 November the Pak army brutally killed 32 innocent persons at village Chhabisha of this upazila; they also set 350 houses on fire. There is a mass grave at Palsa School playground and a memorial sculpture has been established at the Ibrahim Kha College premises.
For details: see ভূঞাপুর উপজেলা, বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ৭।
Religious institutions Mosque 135, temple 7. Noted religious institutions: Kismat Moria Mosque, Falda Jami Mosque, Kalidaha temple.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 43.8%; male 46.6%, female 41.2%. Educational institutions: college 5, secondary school 27, primary school 104, madrasa 21. Noted educational institutions: Ibrahim Kha College (1948), Shamsher Fakir College (1986), Palashia Rani Dinomoni High School (1918), Falda Ramsundar Union High School (1925), Gobindasi High School (1930), Bhuapur Pilot High School (1941), Bhuapur Pilot Girls High School (1941), Bhuapur Fazil Madrasa (1976).
Cultural organisations Club 1, cinema hall 2, library 5,' theatre group 6, literary society 2, cultural organisation 4.
Important installations bangabandhu jamuna multipurpose bridge.
Main sources of income Agriculture 54.61%, non-agircultural labourer 2.45%, industry 1.16%, commerce 14.73%, transport and communication 4.39%, service 9.01%, construction 1.97%, religious service 0.19%, rent and remittance 0.61% and others 10.88%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 62.87%, landless 37.13%. Percentage of ownership of agricultural land is 62.03% in urban area as against 62.99% in rural area.
Main crops Paddy, jute, mustard, wheat, potato, pulse, vegetables.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Peanut, linseed, kaun, sugarcane.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, banana, papaya.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 20, dairy 15 and Poultry 300.
Communication facilities Roads: pucca road 77.42 km, Semi-pucca road 7.39 km, mud road 313.6 km; railway 12 km, waterway 15 km. Bridge 26.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Bullock cart, 'horse carriage, palanquin, dhuli.
Noted manufactories Textile mill, rice mill, still mill, wood furniture factory, agricultural machine factory.
Cottage industries 'Goldsmith, blacksmith, embroidery, woodworks, bamboo work, cane work, nakshi shika.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 16, fairs 6. Bhuapur Hat, Shialkhot Hat, Nikrail Hat, Kuthibayra Hat, Gobindasi Hat, Durgapur Hat are notable.
Main exports Jute, leather, potato, vegetables, mustard.
Access to electricity All the unions of this upazila are under rural electrification net-work; however, 47.8% dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 97.4%, tap 0.2 % and others 2.4%.
Sanitation 59.3% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 36.5% of dwelling houses use non-sanitary latrines; 4.2% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, family planning centre 7, satellite clinic 2, village health centre 14, clinic 3.
NGO activities brac, asa, Serve, caritas, Barendra, SRC, Mukh. [Md Kaiser]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Bhuapur Upazila 2007.
