Ranisankail Upazila: Difference between revisions
No edit summary |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 103: | Line 103: | ||
''NGO activities'' Operationally important NGOs are [[BRAC|brac]], [[RDRS|rdrs]]. [Abu Md. Iqbal Rumi Shah] | ''NGO activities'' Operationally important NGOs are [[BRAC|brac]], [[RDRS|rdrs]]. [Abu Md. Iqbal Rumi Shah] | ||
'''References'' ''Bangladesh Population Census 2001'', Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Ranisankail Upazila 2007. | '''References''' ''Bangladesh Population Census 2001'', Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Ranisankail Upazila 2007. | ||
[[Category:Local Government]] | [[Category:Local Government]] | ||
[[bn:রানীশংকাইল উপজেলা]] | [[bn:রানীশংকাইল উপজেলা]] | ||
Revision as of 11:40, 14 July 2021
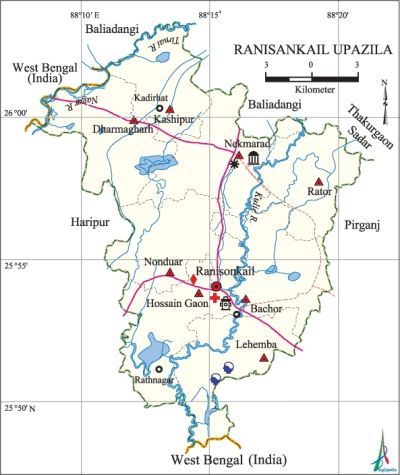
Ranisankail Upazila (thakurgaon district) area 337.80 sq km, located in between 25°48' and 26°04' north latitudes and in between 88°08' and 88°21' east longitudes. It is bounded by baliadangi and thakurgaon sadar upazilas and west bengal state of India on the north, West Bengal state of India on the south, pirganj and Thakurgaon Sadar upazilas on the east, haripur upazila on the west.
Population Total 196134; male 101404, female 94730; Muslim 151890, Hindu 42647, Buddhist 805, Christian 14 and others 778.
Water bodies Main rivers: Kulic, nagar, Tirnai.
Administration Ranisankail Thana, now an upazila, was formed in 1837.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| - | 8 | 124 | 126 | 18853 | 177281 | 581 | 42.1 | 34.4 |
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
| Area (sq km) | Mouza | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||||
| 13.94 | 5 | 18853 | 1352 | 42.1 | ||||
| Union | ||||||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |||||
| Male | Female | |||||||
| Kashipur 55 | 3724 | 8134 | 7750 | 32.67 | ||||
| Dharmagarh 31 | 16841 | 14583 | 13937 | 30.74 | ||||
| Nonduar 71 | 9496 | 12583 | 11975 | 34.23 | ||||
| Nekmarad 79 | 9773 | 12354 | 11304 | 39.37 | ||||
| Bachor 15 | 9057 | 13701 | 12246 | 31.84 | ||||
| Raton 87 | 7989 | 9187 | 8653 | 38.64 | ||||
| Lehemba 63 | 8902 | 13281 | 12337 | 35.27 | ||||
| Hossain Gaon 47 | 18668 | 17581 | 16528 | 38.00 | ||||
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Palace of Raja Tonkonath at Malduar, palace of Raja Birendranath at Jagadal, tomb of Nekmarad Pir Shah Nasiruddin (R), Goraksanath Mandir, Ramrai Dighi, Bangla Garh, Rani Dighi, Shiva Dighi.
Historical events The people of this upazila actively took part in the tebhaga movement. During the war of liberation the Pak army conducted mass killing and plundering in the upazila; they also set many houses on fire.
Marks of the War of Liberation Mass killing site 1 (Khania Dighi).
Religious institutions Mosque 463, temple 20, church 5, tomb 1. Noted religious institutions: Mahal Bari Mosque, Nekmarad Pir Nasiruddin (R) Tomb and Mosque, Goraksanath Mandir.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 35.1%; male 41.2%, female 28.7%. Educational institutions: college 12, technical college 6, secondary school 60, primary school 139, community school 10, madrasa 11. Noted educational institutions: Ranisankail Degree College (1972), Ranisankail Pilot High School (1914), Nekmarad Alimuddin High School (1932), Ranisankail Model Government Primary School (1917), Abad Takia Fazil Madrasa (1976).
Newspapers and periodicals Defunct: Uttar Hath, Asomai.
Cultural organisations Library 63, club 84, theatre group 1, jatra group 1, auditorium 1, cinema hall 4.
Tourist spots Nekmarad, Gorakai, Zamindar Bari at Jagadal, Palace of Raja Tonkonath, Banglagarh.
Main sources of income Agriculture 78.93%, non-agricultural labourer 2.59%, industry 0.51%, commerce 9.1%, transport and communication 1.9%, service 3.24%, construction 0.5%, religious service 0.11%, rent and remittance 0.21% and others 2.91%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 56.95%, landless 43.05%; agricultural landowner: urban 41.14% and rural 58.61%.
Main crops Paddy, wheat, sugarcane, maize, pulse, potato.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Kaun, barley, jute.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, litchi, banana, papaya, watermelon.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Dairy 32, poultry 21.
Communication facilities Pucca road 80 km, mud road 421 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, bullock cart.
Noted manufactories Husking mill 350, oil mill 2, saw mill 8, chira mill 3, ice factory 2, biscuit factory 5, chanachur factory 2, shoe factory 1, welding 11.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, blacksmith, wood work, bamboo work, jute work, tailoring.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 20, fairs 18, most noted of which are Ranisankail Hat, Nekmarad Hat, Balidara Hat, Bharnia Hat, Maharaj Hat, Bagradangi Hat, Council Hat, Sidhar Hat, Gazir Hat, Nekmarad Mela, Gorakai Bannir Mela and Katihar Maghi Mela.
Main exports Paddy, rice, pulse, potato, mango, jackfruit, watermelon, litchi.
Access to electricity All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 10.64% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 96.61%, tap 0.07%, pond 0.24% and others 3.08%.
Sanitation 4.2% (rural 3.3% and urban 12.68%) of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines, 29.22% (rural 27.71% and urban 43.59%) of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines and 66.58% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, satellite clinic 10, union health and family welfare centre 8.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are brac, rdrs. [Abu Md. Iqbal Rumi Shah]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Ranisankail Upazila 2007.
