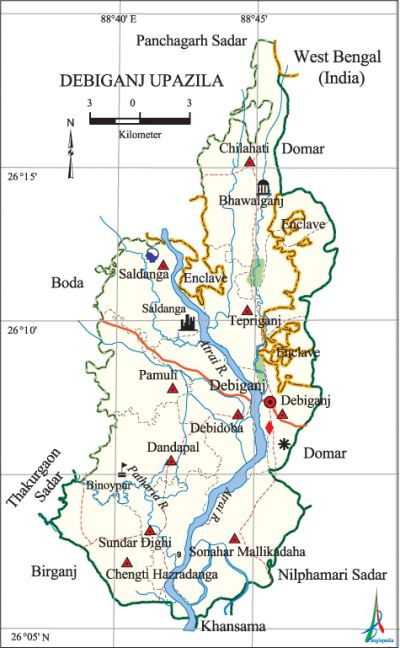
Debiganj Upazila
Debiganj Upazila (panchagarh district) area 309.02 sq km, located in between 26°00' and 26°19' north latitudes and in between 88°39' and 88°49' east longitudes. It is bounded by boda and panchagarh sadar upazilas on the north, birganj, khansama and nilphamari sadar upazilas on the south, domar upazila and west bengal state of India on the east, thakurgaon sadar and Boda upazilas on the west. There are a number of Indian enclaves in the upazila, most noted of which are Behula Danga, Balapara, Court Bhajni and Dahala Khagrabari.
Population Total 224709; male 113120, female 111589; Muslim 166053, Hindu 57944, Buddhist 1, Christian 269 and others 442. Indigenous communities such as santal, oraon and rajbangshi belong to this upazila.
Water bodies Main rivers: karatoya, atrai, Patharia; Sundar Dighi is notable.
Administration Debiganj Thana was formed in 1928 and it was turned into an upazila on 28 March 1983.'
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| - | 10 | 100 | 101 | 15301 | 209408 | 727 | 57.6 | 47.0 |
| Upazila Town | ||||
| Area (sq km) | Mouza | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) |
| 8.76 | 2 | 15301 | 1747 | 57.6 |
| Union | ||||||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |||||
| Male | Female | |||||||
| Chilahati 19 | 12091 | 13006 | 12969 | 52.8 | ||||
| Hazradanga 53 | 6311 | 9256 | 9267 | 47.4 | ||||
| Tepriganj 95 | 9991 | 12396 | 12265 | 43.7 | ||||
| Dandapal 28 | 6665 | 10138 | 10179 | 53.6 | ||||
| Debiganj 47 | 6062 | 14670 | 14193 | 52.1 | ||||
| Debidoba 38 | 7934 | 11222 | 10975 | 50.1 | ||||
| Pamuli 57 | 5280 | 8386 | 8239 | 43.2 | ||||
| Saldanga 66 | 6964 | 9109 | 9113 | 43.0 | ||||
| Sundar Dighi 85 | 5648 | 10170 | 10016 | 51.9 | ||||
| Mallikadaha 76 | 9415 | 14767 | 14373 | 38.7 | ||||
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Revenue office building and residential house of the raja of Kuch Bihar; Jagabandhu Temple, Saldanga Temple.
War of Liberation During the war of liberation in 1971 freedom fighters carried out a number of guerrilla operations at various places of the upazila. The Pak army brutally killed 18 innocent persons at Diagari in November 1971. Debiganj was liberated on 8 December 1971.
For details: see দেবীগঞ্জ উপজেলা, বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ৪।
Religious institutions Mosque 343, temple 26, church 1. Noted religious institutions: Saheb Bari Mosque, Bhailaganj Mosque, Jagabandhu Temple.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 47.7%; male 51.1%, female 44.3%. Noted educational institutions: Debiganj Degree College (1972), Nripendra Narayan Government High School (1906), Sukatu Pradhan High School (1943), Saldanga Bilateral High School (1964), Sonahar High School (1964), Tepriganj Bilateral High School (1965), Pamuli Bilateral' High School (1966), Bagdaha High School (1967), Debiganj Aldini Girls' High School (1970), Pirafata Primary School (1904), Binoypur Primary School (1905), Bhajani Dakhil Madrasa (1982).
Newspapers and periodicals Quarterly: Chhayapath and Purnnabha.
Cultural organisations Club 32, library 1, cinema hall 3, playground 50, women's organisation 1.
Tourist spots China Bangladesh Friendship Bridge, Chandrima Uddayan, Burujer Danga.
Main sources of income Agriculture 77.69%, non-agricultural labourer 3.15%, commerce 9%, transport and communication 2.87%, service 3.01%, construction 0.54%, religious service 0.22%, rent and remittance 0.07% and others 3.45%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 60.49%, landless 39.51%; agricultural landowner: urban 42.16% and rural 61.60%.
Main crops Paddy, jute, wheat, potato, onion, turmeric, ginger, garlic, peanut.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Savory, millet, aus paddy, kaun.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, litchi, papaya, banana, guava.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries This upazila has a number of fisheries, dairies and poultries.'
Communication facilities Roads: pucca 112 km, mud road 436 km; waterway 35 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, bullock cart, horse carriage.
Cottage industries Goldsmith 8, blacksmith 40, potteries 11, weaving 40, embroidery 60, wood work 30.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 40, fair 1, most noted of which are Debiganj, Kaliganj, Bhawlaganj, Saldanga, Dhulajhari, Fulbari, Sona, Lakshmi and Mallikadaha Club's hats.
Main exports Potato, peanut, pebble stone, silicon sand.
Access to electricity All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 21.60% dwellings have access to electricity.
Natural resources Pebble stone, silicon sand.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 96.8%, tap 0.5% and others 2.7%.
Sanitation 45.3% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 36.6% of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 18.1% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, satellite clinic 4, clinic 10, family planning centre 8.
Natural Disasters Many people died of starvation during the famine of 1943. The flood of 1968 caused heavy damages to settlements, livestock and properties of the upazila.
NGO activities brac, asa, CARE, proshika. [Md Ahsan Habib]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Debiganj Upazila 2007.
