Nilphamari Sadar Upazila
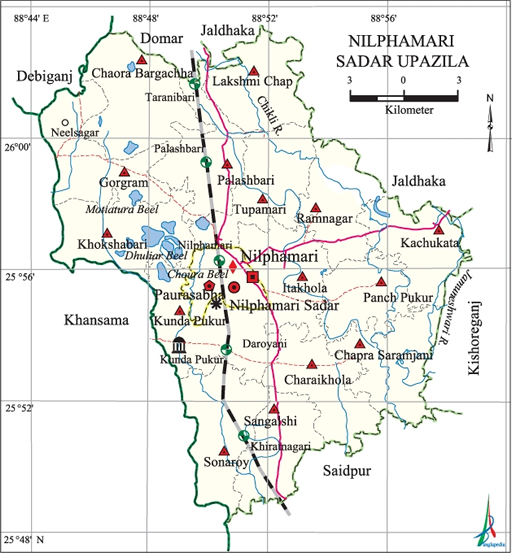
Nilphamari Sadar Upazila (nilphamari district) area 373.30 sq km, located in between 25°48' and 26°03' north latitudes and in between 88°44' and 88°59' east longitudes. It is bounded by domar and jaldhaka upazilas on the north, saidpur upazila on the south, kishoreganj (nilphamari) and Jaldhaka upazilas on the east, khansama and debiganj upazilas on the west.
Population Total 435162; male 219080, female 216082; Muslim 344922, Hindu 89307, Buddhist 8, Christian 518 and others 407.
Water bodies Main rivers: Jamuneshwari, Chikli; Motiatura Beel, Dhuliar Beel, Choura Beel are notable.
Administration Nilphamari Thana was formed in 1870 and it was turned into an upazila in 1984.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| 1 | 15 | 105 | 108 | 45386 | 389776 | 1166 | 64.1 | 43.5 |
| Municipality | ||||||||
| Area (sq km) | Ward | Mahalla | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | |||
| 19.28 | 9 | 13 | 45386 | 2354 | 64.1 | |||
| Union | ||||||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |||||
| Male | Female | |||||||
| Itakhola 31 | 5004 | 14071 | 13834 | 47.1 | ||||
| Kachukata 37 | 5246 | 12797 | 12634 | 44.3 | ||||
| Kunda Pukur 50 | 6597 | 15919 | 15777 | 45.3 | ||||
| Khokshabari 44 | 6451 | 11342 | 11320 | 44.6 | ||||
| Gorgram 25 | 6766 | 14184 | 13730 | 39.5 | ||||
| Chaora Bargachha 18 | 7559 | 12992 | 13400 | 39.7 | ||||
| Charaikhola 12 | 5903 | 15445 | 15342 | 42.1 | ||||
| Chapra Saramjani 11 | 5697 | 13423 | 13604 | 36.3 | ||||
| Tupamari 94 | 5970 | 15207 | 14626 | 45.5 | ||||
| Panch Pukur 63 | 4578 | 11425 | 11032 | 50.0 | ||||
| Palashbari 69 | 5618 | 10513 | 10579 | 40.9 | ||||
| Ramnagar 75 | 5179 | 12287 | 12182 | 40.3 | ||||
| Lakshmi Chap 73 | 5540 | 10052 | 9970 | 43.3 | ||||
| Sangalshi 82 | 4920 | 11525 | 11239 | 46.8 | ||||
| Sonaroy 88 | 6451 | 14612 | 14713 | 46.6 | ||||
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics nilsagar Dighi (former name Birat Dighi or Binni Dighi) at Gorgram, Tomb of Hazrat Pir Mohiuddin (Kunda Pukur), Bishnu Mandir (Palashbari).
War of Liberation On 7 April the freedom fighters captured 300 rifles and 10000 ammunitions from the armory/Treasury. On 8 April the Pak army took control over Nilphamari Town. A joint troop of the freedom fighters and the allied forces had a battle with Pak army at the border between Nilphamari Sadar and neighboring Khansama upazilas in December towards the end of the War of Liberation. Three tanks of the Pak army were destroyed and many Pakistani soldiers were killed in the battle. Two memorial monuments (Swadhinatar Smriti Amlan, Bashar Gate) have been built in the upazila.
For details: see নীলফামারী সদর উপজেলা, বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ৫।
Religious institutions Mosque 624, temple 371, church 1, tomb 2. Noted religious institutions: tomb of Hazrat Pir Mohiuddin (Kunda Pukur), tomb of Syed Pagla Pir (Darowani).
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 45.7%; male 49.4%, female 42.1%. Educational institutions: college 6, primary teachers training institute (PTI) 1, secondary school 87, primary school 217, madrasa 45, maktab 460. Noted educational institutions: Masiur Rahaman College (1958), Government Mohila College (1972), Nilphamari Government College (1986), Nilphamari Government High School (1882), Government Boys' High School (1914), Government Girls' High School (1945), Samir Uddin Boys'; High School (1963), Natun Bazar Bilateral High School (1970), Rabeya Balika Bidya Niketon (1973).
Newspapers and periodicals Daily: Nil Kantha; weekly: Nilphamari Barta, Nilsagar, Nilsamachar; defunct: Jagari (1962), Nilanchan (1972).
Cultural organisations Library 2, club 5, theatre group 4, theatre stage 1, music academy 4, cinema hall 2, women's organisation 1.
Main sources of income Agriculture 69.10%, non-agricultural labourer 3.41%, commerce 12.02%, transport and communication 3.39%, service 5.93%, construction 0.95%, religious service 0.21%, rent and remittance 0.12% and others 4.87%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 55.02%, landless 44.98%; agricultural landowner: urban 40.41% and rural 56.70%.
Main crops Paddy, wheat, jute, potato, tobacco, cotton, ginger.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Linseed, sesame, kaun, mustard, aus paddy.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, blackberry, guava, banana.
Communication facilities Pucca road 241.00 km, mud road 736.42 km; railway 25.06 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, bullock cart.
Noted manufactories Textile mill, saw mill, rice mill, ice cream factory.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, blacksmith, weaving, potteries, bamboo work, wood work, tailoring, bidi factory.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 26, fair 1, most noted of which are Bhabaniganj Hat, Babrijhar Hat, Darowani Hat, Dhelapir Hat, Pancha Pukur Hat, Palashbari Hat, Porardanga Hat, Jadur Hat, Shakhamacha Hat, Syed Pagla Pir Mela at Darwoani.
Main exports Paddy, jute, cotton, ginger, tobacco.
Access to electricity All the wards and unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 36.0% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 96.7%, tap 0.7% and others 2.6%.
Sanitation 29.7% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 44.7% of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 25.6% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres District sadar hospital 1, TB hospital 1, diabetic hospital 1, satellite clinic 2, leprosy hospital 2, union health and family welfare centre 2, family planning centre 15, veterinary hospital 2.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are brac,asa, CARE, Nijera Kori, RDSS. [Abdus Sattar]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Nilphamari Sadar Upazila 2007.
