Feni Sadar Upazila
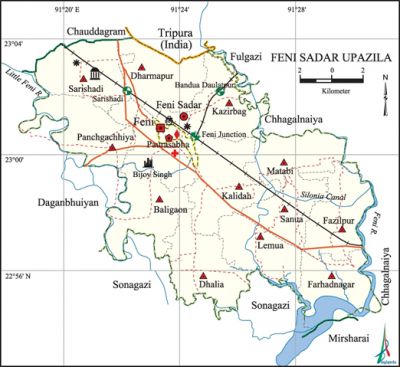
Feni Sadar Upazila (feni district) area 226.19 sq km, located in between 22°54' and 23°04' north latitudes and in between 91°18' and 91°31' east longitudes. It is bounded by tripura state of India, chauddagram, PHulgazi and chhagalnaiya upazilas on the north, sonagazi and mirsharai upazilas on the south, Chhagalnaiya upazila on the east and daganbhuiyan upazila on the west.
Population Total 512646; male 254751, female 257895; Muslim 477777, Hindu 34417, Buddhist 254, Christian 115 and others 83.
Water bodies Main rivers: feni and little feni; Silonia Canal, Bijoy Shingho Dighi, Rajajhi Dighi are notable.
Administration Feni Thana was formed in 1929 and it was turned into an upazila in 1984. Municipality was formed in 1958.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| 1 | 12 | 123 | 125 | 156971 | 355675 | 2266 | 69.7 | 59.8 |
| Municipality | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Ward |
Mahalla |
Population |
Density (per sq km) |
Literacy rate (%) | |||
| 22.00 | 18 | 35 | 156971 | 7135 | 69.7 | |||
| Union | ||||||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |||||
|
Male |
Female | |||||||
| Kazirbag 47 | 4109 | 11529 | 12039 | 63.5 | ||||
| Kalidah 43 | 4938 | 16938 | 15008 | 69.3 | ||||
| Sanua 82 | 3324 | 11002 | 12352 | 59.3 | ||||
| Dharmapur 23 | 3980 | 16674 | 15468 | 61.6 | ||||
| Dhalia 22 | 4301 | 14703 | 15797 | 65.2 | ||||
| Panchgachhiya 64 | 4585 | 20853 | 22615 | 57.1 | ||||
| Farhadnagar 25 | 4187 | 10629 | 12717 | 52.7 | ||||
| Fazilpur 30 | 4278 | 12976 | 14852 | 57.3 | ||||
| Baligaon 20 | 4204 | 16545 | 18120 | 53.8 | ||||
| Matabi 60 | 3610 | 11360 | 12389 | 59.4 | ||||
| Lemua 51 | 3556 | 10478 | 11544 | 61.5 | ||||
| Sarishadi 86 | 5482 | 18510 | 20577 | 58.0 | ||||
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Mosque of Mohammad Ali Chowdhury and Shahi Mosque at Sarishadi, Rajajhi Dighi at Feni (1830), Bijoy Singha Dighi' at Mohipal (1760).
Historical events The Naib Nazim of Dhaka appointed Muhammad Ali Chowdhury as the Fouzdar of Feni in 1762. As a result of his rebellion against the British, Muhammad Ali Chowdhury lost his zamindari in 1790.
War of Liberation During the war of liberation in 1971, the Pak army took control over Feni Sadar upazila on 23 April. They conducted genocide, torture and violation of women; they also set many houses of the upazila on fire. Two major encounters held between the Freedom fighters of the upazila and the Pak army and their collaborators in the upazila were at Dhalia and Daulatpur. There are 7 mass killing sites and one mass grave in Feni Sadar Upazila.
For details: see ফেনী সদর উপজেলা, বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ৬।
Religious institutions Mosque 413, temple 172, church 2, tomb 3. Noted religious institutions: Feni Jami Mosque, Sarishadi Shahi Mosque, Tomb of Pagla Miah, Tomb of Pathan Shah, Ram Singh Smriti Math (1860), Rajbari Temple (1840), Ramkumar Samadhi Math (1902).
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 62.8%; male 64.6%, female 61.1%. Noted educational institutions: Feni Government College (1922), Government Commerce College (1965), Government Zia Mahila College (1979), Feni Public College (1995), Feni Girls' Cadet College (2004), Feni GA Academy (1943), Feni P.T.I (1957), Feni Polytechnic Institute (1962), Feni Teacher's Training College (1963), Feni Government Pilot High School (1886), Feni Government Girls' High School (1910), Kalidah SC High School (1911), Feni Central High School (1919), Feni Model High School (1927), Gobindapur Siddikia Fazil Madrasa (1920), Feni Alia Madrasa (1923).
Newspapers and periodicals Daily: Naya Paigam, Amar Feni; bi-weekly: Path; weekly: Gram Desh, Hawkers, Muhuri, Feni Barta, Feni Prabaha, Feni Sambad, Feni Khabar, Feni Darpan, Feni Times, Ananda Taraka, Shadesh Kantho, Atayeb, Baikali, Fenir Alo, Unmochan, Dristipath, Nabin Alo, Nabin Bangla, Alokito Feni, Nabakiron, Fenir Rabi, Jahur, Kalkantha, Barnamala, Fenir Sastakatha; fortnightly: Masimela, Feni Chitra; monthly: Ananda Bhairabi, Sarasari, Urmi.
Cultural organisations Library 6, club 17, women organisation 2, Shishu Academy 1, music training centre 3, theatre group 7, cinema hall 3, children park 1.
Amusement centres Zila Parishad Children Park, Rajajhi Dighi, Bijoy Shingho Dighi.
Main sources of income Agriculture 20.93%, non-agricultural labourer 2.20%, industry 1.07%, commerce 21.39%, transport and communication 6.04%, service 19.81%, construction 2.52%, religious service 0.40%, rent and remittance 11.94% and others 13.70%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 56.71%, landless 43.29%; agricultural landowner: urban 50.13% and rural 58.61%.'
Main crops Paddy, wheat, pulse, sweet potato, chilli, sugarcane, peanut.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Sesame.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, banana, palm, date.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 12, dairy52 and poultry 240.
Communication facilities Pucca road 265 km, semi-pucca road 58 km, mud road 430 km; railway 26 km; waterway 52 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, bullock cart.
Noted manufactories Textile mill, steel mill, jute mill, oil mill, rice mill, biscuit factory, medicine factory, towel factory, salt factory, cold storage, leather industry, rubber industry.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, wood work, tailoring, bamboo work, cane work.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 40, fairs 3, most noted of which are Sarishadi Bazar, Ranir Hat, Baligaon Bazar, Sanua Bazar; Rath Jatra Mela at Trank Road and' Baishakhi Mela at Mastar Para.
Main exports Towel, mango, salt.
Access to electricity All the wards and unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 82.7% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 84.4%, tap 12.2% and others 3.4%.
Sanitation 73.3% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 25.2% of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 1.5% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Hospital 1, sadar upazila health complex 1, diabetic hospital 1, chest disease clinic 1, trauma centre 1, TB hospital 1, eye hospital 1, CT scan clinic 1, mother and child welfare centre 1, satellite clinic 5, family planning centre 8, seba institute 1, charitable hospital 3, veterinary hospital 1, regional veterinary disease research centre 1, artificial breeding point 1.
Natural disasters The devastating cyclone and tidal bore of 1876 caused huge loss of life and damages to settlements, livestock and other properties of the upazila.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are brac, asa, Swanirvar Bangladesh. [Md Abu Taher Bhuiyan]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Feni Sadar Upazila 2007.
