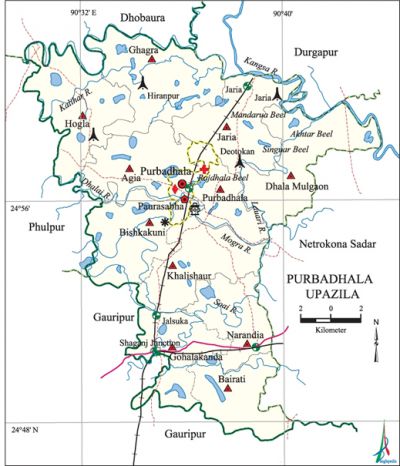
Purbadhala Upazila
Purbadhala Upazila (netrokona district) area 308.03 sq km, located in between 24°48' and 25°04' north latitudes and in between 90°27' and 90°44' east longitudes. It is bounded by durgapur (Netrokona) and dhobaura upazilas on the north, gauripur upazila on the south, netrokona sadar upazila on the east, phulpur and gauripur upazilas on the west.
Population Total 310834; male 153162, female 157672; Muslim 294665, Hindu 14955, Buddhist 15, Christian 585 and others 614. Indigenous community such as garo belongs to this upazila.
Water bodies Main rivers: Dhalai, Soai, Mogra, Kalihar, Kangsa, Lauari; Mandarua, Singuar, Rajdhala and Akhter Beels are notable.
Administration Purbadhala Thana was formed in 1917 and it was turned into an upazila in 1983.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| - | 11 | 226 | 336 | 22132 | 288702 | 1009 | 52.7 | 42.0 |
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Mouza |
Population |
Density (per sq km) |
Literacy rate (%) | ||||
| 7.94 | 3 | 22132 | 2787 | 52.7 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
| Agia 13 | 6626 | 13370 | 14423 | 40.2 |
| Khalishapur 79 | 7700 | 13689 | 14127 | 42.6 |
| Gohalakanda 55 | 5697 | 15543 | 16101 | 48.1 |
| Ghagra 39 | 8938 | 14848 | 15145 | 41.2 |
| Jaria 71 | 5727 | 13939 | 13792 | 38.1 |
| Dhala Mulgaon 31 | 8762 | 14441 | 14625 | 36.8 |
| Narandia 87 | 5553 | 12481 | 12563 | 47.2 |
| Purbadhala 94 | 6058 | 15700 | 15917 | 47.0 |
| Bishkakuni 23 | 7231 | 12766 | 14013 | 42.2 |
| Bairati 15 | 5749 | 10859 | 10994 | 45.7 |
| Hogla 63 | 8177 | 15526 | 15972 | 41.2 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Sunaikandha Mosque, Latirkandha Mosque of Mughal period, ancient temple at Hogla, Zamindar Bari at Baghber and Narayandahar.
Historical events Karam Shah, the founder of the Pagalpanthi doctrine and his son Tipu Shah settled at village Latirkandha of this upazila in 1792 and led the pagal panthi movement and peasant movements from here. Since 1786 they organized anti British movement in alliance with fakir-sannyasi resistance.
War of Liberation The Pak army entered Purbadhala, for the first time, on 29 April 1971. On 1 May the Pak army brutally killed noted physician Dr. Hem Bagchi, his brother-in-law Haridas Sinha and their service assistant Meghu at the courtyard of their residence. Freedom fighters had encounters with the Pak army at Company Goaltala Bazra and some places alongside the Mymensing-Jaria railway track. There is a mass grave at Trimohani of the upazila.
For details: see পূর্বধলা উপজেলা, বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ৬।
Religious institutions Mosque 297, temple 27. Noted religious institutions: Purbadhala Bazar Jami Mosque, Hogla Nrisingh Jeu Akhra Temple.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 42.8%; male 43.9%, female 41.7%. Educational institutions: college 4, secondary school 19, primary school 154, madrasa 12. Noted educational institutions: Purbadhala Degree College (1969), Shaymganj Hafez Ziaur College (1972), Purbadhala Rabeya Ali Mohila College (1994), Purbadhala Jagatmoni Pilot High School (1916), Ghagra High School (1919), N Jaria Zhangail High School (1946), Khalishapur High School (1962), Narayandahar High School (1970), Deotukon High School (1919).
Cultural organisations Library 4, club 33, cinema hall 3, women organisation 1, playground 10, theatre group 1.
Main sources of income Agriculture 75.02%, non-agricultural labourer 3.74%, industry 0.51%, commerce 8.21%, transport and communication 2.44%, service 3.48%, construction 1.01%, religious service 0.22%, rent and remittance 0.18% and others 5.18%.
Main crops Paddy, jute.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Linseed, khesari, kalai, sweet potato, arahar, ginger, turmeric.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, wood-apple, banana, blackberry, lemon.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 4, poultry 26.
Communication facilities Pucca road 60 km, semi-pucca road 3 km, mud road 663 km; waterway 18 km; railway 30 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, horse carriage, bullock cart.
Noted manufactories Flour mill, saw mill, ice factory, welding factory.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, blacksmith, potteries, embroidery, wood work.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 5, fairs 2, most noted of which are Purbadhala Bazar, Hogla Bazar, Ghagra Bazar, Hiranpur Bazar, Shyamganj Bazar, Chaitra Baruni Mela and Samkranti Mela at Purbadhala.
Main exports Paddy, jute, fish.
Access to electricity All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 24.3% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 92.5%, tap 0.3% and others 7.2%. The presence of arsenic has been detected in 33% shallow tube-well water of the upazila.
Sanitation 38.4% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 44.5% of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 17.1% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, family planning centre 11, satellite clinic 3.
Natural disasters 18 members of the Ansar were dead and 81 were seriously wounded due to the tornado of June 1975; it also seriously damaged the Ansar Camp of Jaria.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are brac, proshika, asa, caritas, Shikha. [Syed Marufuzzaman]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Purbadhala Upazila 2007.
