Sarishabari Upazila
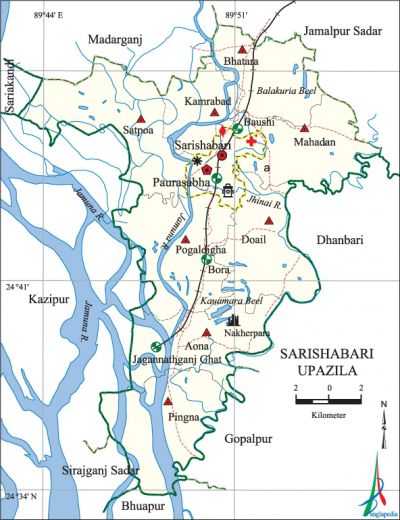
Sarishabari Upazila (jamalpur district) area 263.50 sq km, located in between 24°34' and 24°50' north latitudes and in between 89°43' and 89°56' east longitudes. It is bounded by madarganj and jamalpur sadar upazilas on the north, bhuapur upazila on the south, gopalpur and' dhanbari 'upazilas the east, sariakandi, kazipur and sirajganj sadar upazilas on the west.
Population Total 325320; male 159583, female 165737; Muslim 316774, Hindu 8408, Buddhist 5, Christian 90 and others 43.
Water bodies Main rivers: jamuna, Jhinai; Balakuria Beel and Kauamara Beel are notable.
Administration Sarishabari Thana was formed in 1960 and it was turned into an upazila in 1983.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| 1 | 8 | 117 | 183 | 54177 | 271143 | 1235 | 50.2 (2001) | 42.8 |
| Municipality | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Ward |
Mahalla |
Population |
Density |
Literacy rate (%) | |||
| 21.95 (2001) | 9 | 34 | 52162 | 2218 (2001) | 53.4 | |||
| Upazila Town | ||||
| Area (sq km) | Mouza | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) |
| 2.01 (2001) | 1 | 2015 | 491 (2001) | 44.3 |
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
| Aona 10 | 7552 | 14294 | 15462 | 45.1 |
| Kamrabad 42 | 4269 | 9068 | 9147 | 40.6 |
| Doail 31 | 8244 | 20854 | 22248 | 42.6 |
| Pingna 63 | 7205 | 14010 | 14925 | 40.3 |
| Pogaldigha 73 | 9883 | 26340 | 26662 | 48.8 |
| Bhatara 21 | 6381 | 16135 | 17212 | 45.5 |
| Mahadan 52 | 6563 | 17220 | 18070 | 44.1 |
| Satpoa 84 | 9535 | 15924 | 15587 | 30.0 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Five domed Raspal Jami Mosque (nineteenth century), Narapara Fort (sixteenth century).
War of Liberation Freedom fighters had encounters with Pak army at four places of the upazila. These are Parpara, Baroipatal-fuldaher para, Aramnagar Alia Madrasah and Baushi Bridge. Mass graves had been discovered at 8 places (Baushi bridge area, Muktijoddha Samsad compound, Aramnagar, Outer Signal, Shaicharpara, Kandarpara, Chechiabadha, Pingna Shahi Mosque, Parpara) of the upazila.
For details: see সরিষাবাড়ী উপজেলা, বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ১০।
Religious institutions Mosque 530, temple 19.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 44.6%; male 46.8%, female 42.4%. Educational institutions: college 9, homeopathy college 1, technical college 2, secondary school 35, primary school 117, community school 4, mass education centre 55, madrasa 23. Noted educational institutions: Alhaj Riajuddin Talukder Degree College (1967), Pingna English High School (1879), Pingna High School (1896), Doail High School (1911), Chaparkona Mohesh Chandra High School (1919), Sarishabari Rani Nidmoni Model High School (1920), Sarishabari RDM High School (1920), Balaridia Primary School (1869), Pogaldigha Primary School (1890), Aramnagar Kamil Madrasa (1922), Pingna Madrasa (Emperor Shahjahan's period),
Newspapers and periodicals Weekly: Nabatan.
Cultural organisations Library 76, club 65, theatre group 1, cinema hall 2, women's organisation 32, playground 17.
Main sources of income Agriculture 63.84%, non-agricultural labourer 2.76%, industry 1.31%, commerce 12.29%, transport and communication 2.91%, service 8.06%, construction 1.28%, religious service 0.22%, rent and remittance 0.36% and others 6.97%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 65.90%, landless 34.10%; agricultural landowner: urban 47.56% and rural 69.39%.
Main crops Paddy, jute, wheat, mustard, sugarcane, ground nut, sweet potato, musuri, betel leaf, turmeric, chilli, vegetables.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops China, kaun, sesame, linseed.
Main fruits Mango, coconut, betel nut, banana, papaya.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Dairy 5, poultry 15, hatchery 3, cattle breeding centre 4.
Communication facilities Pucca road 156 km, semi-pucca road 22 km, mud road 352 km; waterway 43 km; railway 37 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, dhuli.
Noted manufactories Jute mill, fertiliser factory, welding factory.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, blacksmith, potteries, weaving, nakshi kantha, wood work, bamboo work, cane work, jute and cotton work.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 60, fairs 3, most noted of which are Aramnagar Hat, Boira Hat, Pingna Hat, Bhatara Hat, Bagarpar Mela and Baushi Panchapir Mela.
Main exports Jute, jute made goods, mustard, rice, chilli, fertiliser, milk.
Access to electricity All the wards and unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 55.6% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 94.7%, tap 2.8% and others 2.5%. The presence of arsenic has been detected in shallow tube-well water of the upazila.
Sanitation 52.5% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 39.0% of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 8.5% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, family planning centre 8, satellite clinic 4, diagnostic centre 2.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are brac, asa, caritas, CARE, DANIDA. [Sayed Md. Abdullah Al Mamun Chowdhury]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Sarishabari Upazila 2007.
