Bahubal Upazila: Difference between revisions
(Content Updated.) |
No edit summary |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Bahubal Upazila''' ([[Habiganj District|habiganj district]]) area 250. | '''Bahubal Upazila''' ([[Habiganj District|habiganj district]]) area 250.65 sq km, located in between 24°15' and 24°28' north latitudes and in between 91°28' and 91°37' east longitudes. It is bounded by [[Nabiganj Upazila|nabiganj]] upazila on the north, [[Chunarughat Upazila|chunarughat]] upazila on the south, [[Sreemangal Upazila|sreemangal]] upazila on the east, [[Habiganj Sadar Upazila|habiganj]][[Habiganj Sadar Upazila| Sadar]] upazila on the west. | ||
''Population'' Total | ''Population'' Total 197997; male 98101, female 99896; Muslim 168819, Hindu 28471, Buddhist 6, Christian 579 and others 122. Indigenous communities such as khasia, Tipra and manipuri belong to this upazila. | ||
''Water bodies'' Main rivers: Korangi, Khowai, [[Barak River|barak]]. | ''Water bodies'' Main rivers: Korangi, Khowai, [[Barak River|barak]]. | ||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
| Urban || Rural || | Urban || Rural | | Urban || Rural || | Urban || Rural | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | - || 7 || 140 || 342 || 4045 || 193952 || 790 || 56.1 || 39.4 | ||
- | |||
| | |||
7 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 65: | Line 39: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | 2.11 || 2 || 4045 || 1917 || 56.1 | ||
2. | |||
| | |||
2 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|} | |} | ||
{| class="table table-bordered table-hover" | {| class="table table-bordered table-hover" | ||
| Line 87: | Line 48: | ||
| Male || Female | | Male || Female | ||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Putijuri 59 || 13853 || 13294 || 13482 || 48.5 | ||
Putijuri 59 | |||
| | |||
13853 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Bahubal 11 || 4997 || 14448 || 14561 || 36.1 | ||
Bahubal 11 | |||
| | |||
4997 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
36. | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Bhadeshwar 23 || 15114 || 17144 || 17005 || 37.8 | ||
Bhadeshwar 23 | |||
| | |||
15114 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Mirpur 47 || 4068 || 12703 || 13203 || 48.0 | ||
Mirpur 47 | |||
| | |||
4068 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Lamatashi 35 || 5048 || 11043 || 11734 || 40.6 | ||
Lamatashi 35 | |||
| | |||
5048 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Satkapan 71 || 11366 || 16635 || 16720 || 33.2 | ||
Satkapan 71 | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
| | |||
|- | |- | ||
| | | Snanghat 83 || 11029 || 12834 || 13191 || 36.6 | ||
Snanghat 83 | |} | ||
''Source'' Bangladesh Population Census 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics. | |||
| | [[Image:BahubalUpazila.jpg|thumb|400px|right]] | ||
| | |||
''Historical events'' Afghan Chief Khwaja Osman left Bukai Nagar Fort and established shelter at Putijuri of present Bahubal upazila on the foot of the Giripal. He built a fort there which had strategic importance for defense. However, the Mughal took the advantage of the fort when his brother evacuated it. Finally the Khwaja Osman's army was defeated at village Dhalamvapur of Maulvi Bazar district about 9 to 10 km on the east. | |||
'' | |||
''War of Liberation'' Freedom fighters did not have any direct encounter with the Pak army in the upazila. But they often joined freedom fighters of nearby upazilas and fought against enemies at places like Rema Tea Garden, Kalenga and Sherpur. Bahubal was liberated on 6 december 1971. A memorial monument has been built at the mass killing site at Foyjabad. | |||
'' | |||
'' | For details: see বাহুবল উপজেলা, ''বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ'' (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ৭। | ||
''Literacy rate and educational institutions'' Average literacy | ''Literacy rate and educational institutions'' Average literacy 39.8%; male 41.2%, female 38.4%. Educational institutions: college 2, secondary school 30, primary school 148, kindergarten 4, madrasa 25. Noted educational institutions: Alif Sobhan College, Dina Nath Institute (1937), Faizunechha High School (1960), Putijuri SC High School, Manab Kallayan High School (1941), Mirpur Dakhil Madrasa (1920). | ||
''Cultural organisations'' Library 5, club 12, community centre 1, auditorium 1, literary society 2, play ground 8. | ''Cultural organisations'' Library 5, club 12, community centre 1, auditorium 1, literary society 2, play ground 8. | ||
| Line 220: | Line 88: | ||
''Fisheries, dairies and poultries'' This upazila has a number of fisheries, dairies and poultries.' | ''Fisheries, dairies and poultries'' This upazila has a number of fisheries, dairies and poultries.' | ||
''Communication facilities'' Roads: pucca road | ''Communication facilities'' Roads: pucca road 85.27 km, semi-pucca road 7.06 km, mud road 496.62 km; waterways 12 km; railways 13 km. | ||
''Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport'' Palanquin, soari boat. | ''Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport'' Palanquin, soari boat. | ||
| Line 230: | Line 98: | ||
''Main exports'' Paddy, tea, pineapple, lemon, jackfruit, wood, rubber. | ''Main exports'' Paddy, tea, pineapple, lemon, jackfruit, wood, rubber. | ||
''Access to electricity'' All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However | ''Access to electricity'' All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 39.0% dwellings have access to electricity. | ||
Natural resources' Natural gas, sand. | ''Natural resources'' Natural gas, sand. | ||
''Sources of drinking water'' Tube-well | ''Sources of drinking water'' Tube-well 91.3%, tap 0.5% and others 8.2%. | ||
''Sanitation'' | ''Sanitation'' 47.0% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 45.5% of dwelling houses use non-sanitary latrines; 7.5% of households do not have latrine facilities. | ||
''Health centres'' Upazila health complex 1, union health and family planning centre 7, community clinic 3, private clinic 1, mother and child welfare centre 5, charity hospital 1, satellite clinic 1, diagnostic centre 2, veterinary hospital 1. | ''Health centres'' Upazila health complex 1, union health and family planning centre 7, community clinic 3, private clinic 1, mother and child welfare centre 5, charity hospital 1, satellite clinic 1, diagnostic centre 2, veterinary hospital 1. | ||
| Line 242: | Line 110: | ||
''NGO activities'' [[BRAC|brac]],[[Asa| asa]], CARE. [Jayanta Singh Roy] | ''NGO activities'' [[BRAC|brac]],[[Asa| asa]], CARE. [Jayanta Singh Roy] | ||
'''References''' Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Bahubal Upazila 2007. | '''References''' Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Bahubal Upazila 2007. | ||
[[Category:Upazilas of Bangladesh]] | [[Category:Upazilas of Bangladesh]] | ||
Latest revision as of 18:43, 14 October 2023
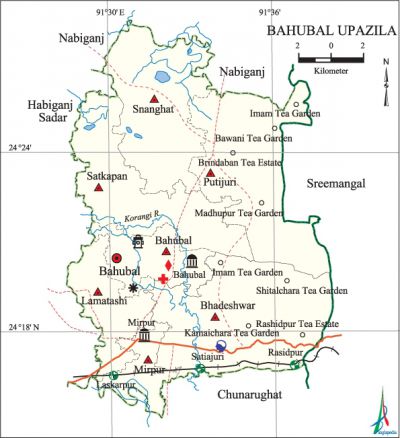
Bahubal Upazila (habiganj district) area 250.65 sq km, located in between 24°15' and 24°28' north latitudes and in between 91°28' and 91°37' east longitudes. It is bounded by nabiganj upazila on the north, chunarughat upazila on the south, sreemangal upazila on the east, habiganj Sadar upazila on the west.
Population Total 197997; male 98101, female 99896; Muslim 168819, Hindu 28471, Buddhist 6, Christian 579 and others 122. Indigenous communities such as khasia, Tipra and manipuri belong to this upazila.
Water bodies Main rivers: Korangi, Khowai, barak.
Administration Bahubal Thana, now an upazila, was formed in 1921.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| - | 7 | 140 | 342 | 4045 | 193952 | 790 | 56.1 | 39.4 |
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Mouza |
Population |
Density |
Literacy rate (%) | ||||
| 2.11 | 2 | 4045 | 1917 | 56.1 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
| Putijuri 59 | 13853 | 13294 | 13482 | 48.5 |
| Bahubal 11 | 4997 | 14448 | 14561 | 36.1 |
| Bhadeshwar 23 | 15114 | 17144 | 17005 | 37.8 |
| Mirpur 47 | 4068 | 12703 | 13203 | 48.0 |
| Lamatashi 35 | 5048 | 11043 | 11734 | 40.6 |
| Satkapan 71 | 11366 | 16635 | 16720 | 33.2 |
| Snanghat 83 | 11029 | 12834 | 13191 | 36.6 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Historical events Afghan Chief Khwaja Osman left Bukai Nagar Fort and established shelter at Putijuri of present Bahubal upazila on the foot of the Giripal. He built a fort there which had strategic importance for defense. However, the Mughal took the advantage of the fort when his brother evacuated it. Finally the Khwaja Osman's army was defeated at village Dhalamvapur of Maulvi Bazar district about 9 to 10 km on the east.
War of Liberation Freedom fighters did not have any direct encounter with the Pak army in the upazila. But they often joined freedom fighters of nearby upazilas and fought against enemies at places like Rema Tea Garden, Kalenga and Sherpur. Bahubal was liberated on 6 december 1971. A memorial monument has been built at the mass killing site at Foyjabad.
For details: see বাহুবল উপজেলা, বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ৭।
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 39.8%; male 41.2%, female 38.4%. Educational institutions: college 2, secondary school 30, primary school 148, kindergarten 4, madrasa 25. Noted educational institutions: Alif Sobhan College, Dina Nath Institute (1937), Faizunechha High School (1960), Putijuri SC High School, Manab Kallayan High School (1941), Mirpur Dakhil Madrasa (1920).
Cultural organisations Library 5, club 12, community centre 1, auditorium 1, literary society 2, play ground 8.
Main sources of income Agriculture 62.71%, non-agricultural labourer 10.88%, commerce 8.17%, transport and communication 1.85%, service 3.92%, construction 0.55%, religious service 0.39%, rent and remittance 1.68% and others 9.85%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 57.09%, landless 42.91%; agricultural landowner: urban 53.44% and rural 57.17%.
Main crops Paddy, mustard seed, tea, wheat, rubber, betel leaf, peanut, oil seed, vegetables.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Sesame, sweet potato, jute.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, banana, litchi, lemon, pineapple.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries This upazila has a number of fisheries, dairies and poultries.'
Communication facilities Roads: pucca road 85.27 km, semi-pucca road 7.06 km, mud road 496.62 km; waterways 12 km; railways 13 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, soari boat.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, blacksmith, potteries.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 12, fairs 3, most noted of which are Putijuri Bazar, Bahubal Bazar, Mirpur Bazar, Chandrachurir Mela and Dhannakhalir Mela.
Main exports Paddy, tea, pineapple, lemon, jackfruit, wood, rubber.
Access to electricity All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 39.0% dwellings have access to electricity.
Natural resources Natural gas, sand.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 91.3%, tap 0.5% and others 8.2%.
Sanitation 47.0% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 45.5% of dwelling houses use non-sanitary latrines; 7.5% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, union health and family planning centre 7, community clinic 3, private clinic 1, mother and child welfare centre 5, charity hospital 1, satellite clinic 1, diagnostic centre 2, veterinary hospital 1.
NGO activities brac, asa, CARE. [Jayanta Singh Roy]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Bahubal Upazila 2007.
