Gaffargaon Upazila
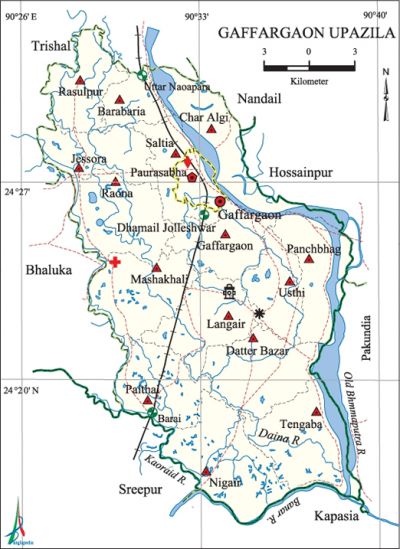
Gaffargaon Upazila (mymensingh district) area 401.16 sq km, located in between 24°15' and 24°33' north latitudes and in between 90°27' and 90°39' east longitudes. It is bounded by trishal and nandail upazilas on the north, kapasia and sreepur (gazipur) upazilas on the south, hossainpur and pakundia upazilas on the east, Trishal, bhaluka and Sreepur (Gazipur) upazilas on the west.
Population Total 413488; male 211195, female 202293; Muslim 406786, Hindu 6256 and others 446.
Water bodies Main rivers: old brahmaputra and Kaoraid; Raona, Taltala, Subi, Mulapalia, Baragup and Hoara beels are notable.
Administration Gaffargaon Thana was formed in 1897 and it was turned into an upazila in 1983.'
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
|
1 |
15 |
202 |
212 |
32997 |
380491 |
1031 |
54.8 |
45.6 |
| Municipality | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Ward |
Mahalla |
Population |
Density |
Literacy rate (%) | |||
|
5.39 |
9 |
19 |
21937 |
4070 |
57.7 | |||
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Mouza |
Population |
Density |
Literacy rate (%) | ||||
|
6.82 |
6 |
11060 |
1622 |
48.9 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
|
Usthi 94 |
4807 |
11503 |
11250 |
43.62 |
|
Gaffargaon 25 |
5585 |
14163 |
13917 |
48.24 |
|
Char Algi 12 |
7956 |
14433 |
13431 |
34.76 |
|
Tengaba 88 |
8354 |
15493 |
4654 |
55.25 |
|
Datter Bazar 18 |
7637 |
14969 |
14478 |
52.57 |
|
Nigair 50 |
8407 |
16963 |
16300 |
51.49 |
|
Paithal 56 |
6412 |
12211 |
11768 |
45.67 |
|
Panchbhag 63 |
6452 |
13839 |
13339 |
42.44 |
|
Barabaria 11 |
2993 |
8899 |
8836 |
38.37 |
|
Mashakhali 44 |
7719 |
14709 |
14288 |
46.02 |
|
Jessora 31 |
5440 |
12036 |
11622 |
42.77 |
|
Rasulpur 69 |
5317 |
11504 |
11224 |
39.21 |
|
Raona 75 |
7032 |
12779 |
12371 |
42.18 |
|
Langair 37 |
6712 |
12580 |
12090 |
49.52 |
|
Saltia 82 |
5965 |
13420 |
12482 |
45.67
|
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Tomb and dighi of Kalu Shah, Dui Satiner Dighi (dighi of two fellow wives), Dighir Par Mosque (1392 AD), Lakshmi Narayan Jeu Mandir (1335 BS), Kali Mandir at Shibganj (Sultanate period).
Historical events During the fakir-sannyasi resistance movement in 1766 there was one abode of the sanyasis and a dargah of Shah Madar at village Dubhasia of Gaffargaon upazila. In 1800, Aratun, an Armenian, first established a Neelkuthi in Gaffargaon town. In order to get rid of suppression of indigo planters, the people of the upazila participated in the indigo resistance movement. On 17 April 1971 two fighter planes of the Pakistan army opened fire by machine gun on Gaffargaon in which 17 people were killed and more than one hundred were wounded.
Marks of the War of Liberation Mass killing site 2 (Launch Ghat near the Bazar and at Char Algi Union), memorial monument 1.
Religious institutions Mosque 612, temple 12, tomb 3.Noted religious institutions: Mosque of Ghiyasuddin Azam Shah at Dighir Par, Gaffargaon Station Mosque, Gayeshpur Bazar Jami Mosque, Sutar Chap Jami Mosque, Panchbhag Jami Mosque, Atharodana Sheikhbari Mosque, Malmal Sarkerbari Mosque, Satarbari Miahbari Mosque, Lakshmi Narayan Jeo Mandir, Shibganj Kali Mandir.'
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 46.4%; male 47.2%, female 45.5%. Educational institutions: college 8, secondary school 77, primary school 329, community school 26. Noted educational institutions: Dhala High School (1893), Gaffargaon Islamia Government High School (1902), Biroi Taltala Girls' High School (1902), Kandipara Askar High School (1906), Shibganj B Das High School (1915), Dhanikhola' Osmania Multilateral High School (1916), Panchbhag Islamia Fazil Madrasa (1921), Maisbari Dhakhil Madrasa (1918).
Newspapers and periodicals Defunct: Anirban, Pous, Agnishila (monthly), Amader Kagaj (quarterly).
Cultural organisations Club 80, library 6, cinema hall 7, theatre group 1.
Main sources of income Agriculture 64.14%, non-agricultural labourer 3.24%, industry 0.47%, commerce 11.36%, transport and communication 2.75%, service 7.59%, construction 1.05%, religious service 0.25%, rent and remittance 1.19% and others 7.96%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 67.56%, landless 32.44%; agricultural landowner: urban 49.81% and rural 68.98%.
Main crops Paddy, jute, wheat, potato, ground nut, sugarcane, mustard, vegetables.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Sesame.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, black berry, litchi, papaya, banana.
Communication facilities Pucca road 90 km, semi-pucca road 4 km, mud road 450 km; waterway 108 nautical miles; railway 23 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, horse carriage.
Noted manufactories Rice mill, flour mill, oil mill, saw mill, printing press, ice factory, soap factory.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, weaving, blacksmith, embroidery, bamboo work, wood work.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 57, most noted of which are Salti Bazar, Dutter Bazar and Mukhir Mela.
Main exports Paddy, jute.
Access to electricity All the wards and unions of the upazila are under rural electrification network. However 12.62% of the dwellings have access to electricity.'
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 90.23%, tap 0.34%, pond 1% and others 8.43%.
Sanitation 18.43% (rural 15.87% and urban 50.59%) of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 54.24% (rural 56.17% and urban 29.97%) of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 27.33% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, rural medical centre 4, family welfare centre 9.
Natural disasters Three fourth of the total area of Gaffargaon upazila was submerged into water during the floods of 1954 and 1955; it also caused huge damages to settlements and properties of the upazila.
NGO activities brac, asa, proshika, SSS. [Shafiqul Kader]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Gaffargaon Upazila 2007.
