Madhabpur Upazila
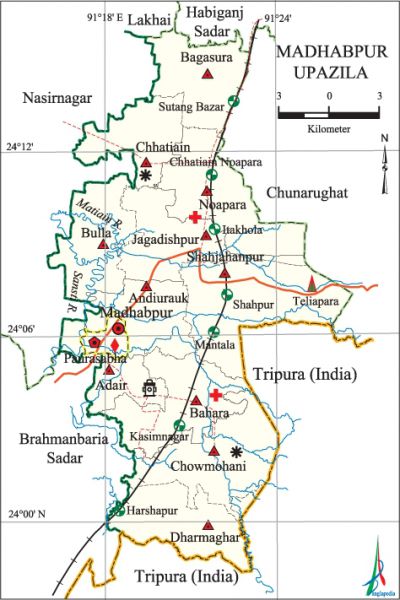
Madhabpur Upazila (habiganj district) area 294.28 sq km, located in between 23°58' and 24°16' north latitudes and in between 91°16' and 91°25' east longitudes. It is bounded by lakhai and habiganj sadar upazilas on the north, tripura State of India on the south, chunarughat upazila and Tripura State of India on the east, brahmanbaria sadar and nasirnagar upazilas on the west.
Population Total 272578; male 138143, female 134535; Muslim 216510, Hindu 55235, Buddhist 659, Christian 13 and others 161.
Water bodies Main rivers: Matiain, Sansti.
Administration Madhabpur Thana, now an upazila, was formed in 1804.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
|
1 |
11 |
181 |
268 |
18802 |
253776 |
926 |
47.95 |
44.94 |
| Municipality | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Ward |
Mahalla |
Population |
Density (per sq km) |
Literacy rate (%) | |||
|
7.01 |
9 |
12 |
16646 |
2676 |
23.73 | |||
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Mouza |
Population |
Density (per sq km) |
Literacy rate (%) | ||||
|
1.31 |
2 |
2156 |
1646 |
71.41 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female
| |||
|
Adair 16 |
3772 |
8231 |
8028 |
34.24 |
|
Andiurauk 77 |
6059 |
8403 |
8050 |
49.48 |
|
Chowmohani 51 |
8025 |
10561 |
14933 |
41.64 |
|
Chhatiain 43 |
5078 |
10509 |
10214 |
41.72 |
|
Jagadishpur 69 |
5871 |
11998 |
11753 |
41.50 |
|
Dharmaghar 60 |
6822 |
12077 |
12088 |
44.90 |
|
Noapara 86 |
7550 |
13365 |
12780 |
41.42 |
|
Bagasura 17 |
5822 |
12344 |
11669 |
42.99 |
|
Bahara 25 |
7053 |
14616 |
14437 |
38.46 |
|
Bulla 34 |
6257 |
7931 |
8286 |
34.33 |
|
Shahjahanpur 94 |
10405 |
14780 |
14379 |
42.85 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
History of the War of Liberation On 4 April 1971, mohammad ataul ghani osmany (supreme commander of the war of liberation and some officers of the 2nd and 4th East Bengal Regiment assembled in the Teliapara Tea Garden Dakbungalow and discussed different aspects of the War of Liberation.
Marks of the War of Liberation Mass killing site 1, memorial monument 1 (Taliapara).
Religious institutions Mosque 254, temple 7, tomb 5.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 42.12%; male 47.67%, female 36.52%. Educational institutions: college 2, secondary school 10, primary school 119, community school 2, kindergarten 3, madrasa 8. Noted educational institutions: Govindapur Government High School (1832), Adair Loknath High School (1911), Chhatiain Biswanath High School (1921), Jagadishpur JC High School (1924), Auliabad RK High School, Harashpur Darul Ulum Islamia Madrasa.
Cultural organisations Library 3, club 8, cinema hall 2, auditorium 1, literary organisation 5, women's organisation 1, playground 5.
Important installations and Tourists spots Shahji Bazar Power Plant and tea gardens at Noapara, Jagadishpur, Taliapara and Surma.
Main sources of income Agriculture 61.43%, non-agricultural labourer 4.38%, commerce 10.79%, transport and communication 1.51%, service 6.82%, construction 0.71%, religious service 0.35%, rent and remittance 1.48% and others 12.53%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 57.37%, landless 42.63%; agricultural landowner: urban 51.62% and rural 57.76%.
Main crops Paddy, potato, jute, mustard, pulse, wheat.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Sesame, sweet potato, linseed, kaun.Main fruits Mango, blackberry, papaya, coconut, jackfruit.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 16, dairy 11.
Communication facilities Pucca road 35 km, mud road 778 km; railway 40 km; waterway 160 nautical miles.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, horse carriage, bullock cart.
Noted manufactories Power plant, textile mill, soap factory, candle factory.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 28, fair 1, most noted of which are Madhabpur Bazar, Noapara Bazar, Taliapara Bazar, Mantala Bazar, Jagadishpur Bazar, Dharmaghar Bazar.
Main exports Paddy, jute.
Access to electricity All the wards and unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 26.61% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Natural resources Natural gas and silicate sand.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 90.44%, tap 1.37%, pond 2.54% and others 5.65%.
Sanitation 28.13% (rural 26.59% and urban 50.47%) of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 58.32% (rural 59.14% and urban 43.86%) of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 13.55% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, union health and family welfare centre 6, family planning centre 6, community clinic 2, private clinic 1, mother and child welfare centre 2, maternity 6, charitable dispensary 2, satellite clinic 1, diagnostic centre 1, veterinary hospital 1.
NGO activities Operationally important NGOs are brac, Vision, asa. [A.B.M Masud Laskar]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Field report of Madhabpur Upazila 2010.
