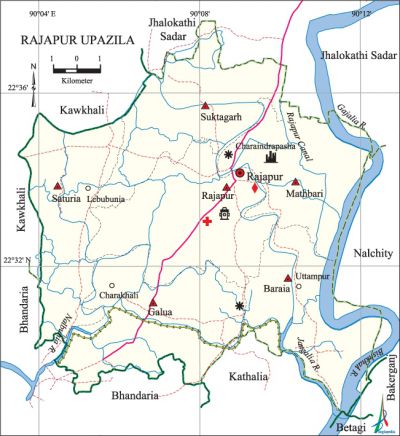
Rajapur Upazila
Rajapur Upazila (jhalokati district) area 164.33 sq km, located in between 22°29' and 22°38' north latitudes and in between 90°03' and 90°13' east longitudes. It is bounded by jhalokati sadar and kawkhali (pirojpur) upazilas on the north, bhandaria, kanthalia and betagi upazilas on the south, nalchity and bakerganj upazilas and Gajalia river on the east, Bhandaria and Kawkhali upazilas on the west.
Population Total 149332; male 74072, female 75260; Muslim 139937, Hindu 9367, Christian 19 and others 9.
Water bodies Main rivers: Gajalia, bishkhali, Nalbunia, jangalia; Rajapur Canal is notable.
Administration Rajapur Thana was formed in 1920 and it was turned into an upazila in 1983.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
|
- |
6 |
72 |
75 |
13597 |
135735 |
909 |
74.1 |
67.4 |
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area (sq km) |
Mouza |
Population |
Density (per sq km) |
Literacy rate (%) | ||||
|
9.75 |
3 |
13597 |
1395 |
74.1 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female
| |||
|
Galua 27 |
5750 |
16646 |
17216 |
66.95 |
|
Baraia 13 |
6738 |
11189 |
10721 |
61.50 |
|
Mathbari 40 |
6355 |
10466 |
11035 |
64.13 |
|
Rajapur 54 |
7391 |
16202 |
16632 |
72.19 |
|
Saturia 67 |
6137 |
9399 |
9350 |
73.42 |
|
Suktagarh 81 |
6476 |
10170 |
10306 |
69.10 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Surichora Jami Mosque (Mughal period), Sujabad Qilla (Mughal period).
History of the War of Liberation On 21 October 1971 a battle was fought between the freedom fighters and the Pak army at the Rajapur upazila compound in which 8 Pak soldiers were killed and so were 3 freedom fighters. On 27 November the freedom fighters raided the Rajapur Police Station and took control of it. This upazila was liberated on 27 November.
Religious institutions Mosque 441, temple 54, eidgah 21. Noted religious institutions: Surichora Jami Mosque.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 68%; male 70.6%, female 65.6%. Educational institutions: college 4, secondary school 55, primary school 106, community school 14, madrasa 10. Noted educational institutions: Rajapur Degree College, Rajapur Pilot High School (1926), Afaj Uddin Girls' High School, Saturia Secondary School, Galua Secondary School, Nijamia Secondary School, Karimannesa Girls' School, Rajapur Fazil Madrasa (1940).
Newspapers and periodicals Dhansiri Shahitya Saikat (1992).
Cultural organisations Library 32, club 67, women's organisation 1, orphanage 20, cultural group 2, community centre 1, cinema hall 1, playground 10.
Main sources of income Agriculture 52.37%, non-agricultural labourer 4.98%, industry 0.84%, commerce 14.38%, transport and communication 2.63%, service 13.4%, construction 2.03%, religious service 0.42%, rent and remittance 2.42% and others 6.53%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 72%, landless 28%; agricultural landowner: urban 64.92% and rural 72.67%.
Main crops Paddy, wheat, pulse, betel leaf, vegetables.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Mustard, sesame, sugarcane, sweet potato.
Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, betel nut, banana, hog plum, coconut, litchi.
Fisheries, dairies and poultries Fishery 5, dairy 1, poultry 30.
Communication facilities Pucca road 36 km, semi-pucca road 54 km, mud road 482 km; waterway 7 nautical miles.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin.
Noted manufactories Rice mill, bidi factory, welding factory.
Cottage industries Weaving, bamboo work, tailoring.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 35, fairs 7, most noted of which are Lebu Bunia Hat, Balar Jore Hat, Charkhali Hat, Baghri Hat, Uttampur Hat and Badur Tala Hat.
Main exports Banana, coconut, betel leaf, betel nut.
Access to electricity All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 17.6% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 92.95%, tap 0.12%, pond 5.49% and others 1.44%. The presence of arsenic has been detected in shallow tube-well water of the upazila.
Sanitation 71.43% (rural 69.85% and urban 88.11%) of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 25.31% (rural 27.13% and urban 6.08%) of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 3.26% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health complex 1, family planning centre 5, satellite clinic 1, community clinic 16.
Natural disasters Many people were victims of the flood of 1786 and cyclones and tidal bore of 1822, 1909 and 1970. These natural disasters also caused heavy damages to settlements, livestock and crops of the upazila.
NGO activities Operationally important NGO is Integrated Social Development Project. [Muhammad Golam Mustafa Siddiqui]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Rajapur Upazila 2007.
