Bangladesh: Difference between revisions
(Content Updated.) |
No edit summary |
||
| (5 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
'''Bangladesh''' emerged as an independent and sovereign country on 16 December 1971 following a nine-month [[War of Liberation, The|war of liberation]]. Dhaka (previously spelt Dacca) is its capital. | '''Bangladesh''' emerged as an independent and sovereign country on 16 December 1971 following a nine-month [[War of Liberation, The|war of liberation]]. Dhaka (previously spelt Dacca) is its capital. | ||
''''' | '''''Information Brief''''' | ||
''Official name'' People's Republic of Bangladesh (Gana Prajatantri Bangladesh). | ''Official name'' People's Republic of Bangladesh (Gana Prajatantri Bangladesh). | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
''Area and boundaries'' Area: 147,570 sq km. Boundaries: [[West Bengal|west bengal]] (India) on the west; West Bengal, [[Assam|assam]] and Meghalaya (all the Indian states) on the north; Indian states of Assam, [[Tripura|tripura]] and Mizoram together with Myanmar on the east; and [[Bay of Bengal|bay of bengal]] on the south. The total length of the land border is about 4,246 km, of which 93.9% is shared with India and the rest 6% with Myanmar. Limit of territorial water is 12 nautical miles (22.22 km) and the area of the high seas extending to 200 nautical miles (370.40 km) measured from the baselines constitutes the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ). | ''Area and boundaries'' Area: 147,570 sq km. Boundaries: [[West Bengal|west bengal]] (India) on the west; West Bengal, [[Assam|assam]] and Meghalaya (all the Indian states) on the north; Indian states of Assam, [[Tripura|tripura]] and Mizoram together with Myanmar on the east; and [[Bay of Bengal|bay of bengal]] on the south. The total length of the land border is about 4,246 km, of which 93.9% is shared with India and the rest 6% with Myanmar. Limit of territorial water is 12 nautical miles (22.22 km) and the area of the high seas extending to 200 nautical miles (370.40 km) measured from the baselines constitutes the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ). | ||
''Administrative units'' division | ''Administrative units'' division 8 ([[Dhaka Division|dhaka]], [[Chittagong Division|chittagong]], [[Khulna Division|khulna]], [[Rajshahi Division|rajshahi]], [[Barisal Division|barisal]], [[Sylhet Division|sylhet]], [[Rangpur Division|rangpur]] and Mymensingh); district 64; upazila 495 and thana 652 (2022), union 4,578 (2022), mouza 59,990, village 87,362; city corporation 12 (Dhaka North City Corporation, Dhaka South City Corporation, [[Chittagong City Corporation|chittagong city corporation]], [[Khulna City Corporation|khulna city corporation]], [[Rajshahi City Corporation|rajshahi city corporation]], [[Sylhet City Corporation|sylhet city corporation]], [[Barisal City Corporation|barisal city corporation]], Rangpur City Corporation, Mymensingh City Corporation, [[Narayanganj City Corporation|narayanganj city corporation]], [[Comilla City Corporation|comilla city corporation]], Gazipur City Corporation); municipality 331 (2022). | ||
''Physiography'' A humid lowlying alluvial region, Bangladesh is composed mainly of the great combined [[Delta|delta]] of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna rivers. It is one of the largest deltas in the world. The monotony of flatness has been relieved inland by two elevated tracts - the [[Madhupur Tract|madhupur]] and the [[Barind Tract|barind tracts]], and on the northeast and southeast by rows of hills. Some 75% of the land is less than 3m above mean sea level (MSL) and vulnerable to floods and cyclones. The maximum elevation is 1,280m above MSL at Saichal Range in [[Rangamati District|rangamati]] district. Tajingdong is the highest peak and called as Bijoy. | ''Physiography'' A humid lowlying alluvial region, Bangladesh is composed mainly of the great combined [[Delta|delta]] of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna rivers. It is one of the largest deltas in the world. The monotony of flatness has been relieved inland by two elevated tracts - the [[Madhupur Tract|madhupur]] and the [[Barind Tract|barind tracts]], and on the northeast and southeast by rows of hills. Some 75% of the land is less than 3m above mean sea level (MSL) and vulnerable to floods and cyclones. The maximum elevation is 1,280m above MSL at Saichal Range in [[Rangamati District|rangamati]] district. Tajingdong is the highest peak and called as Bijoy. | ||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
''Tourist spots'' [[Cox's Bazar|cox's bazar]], [[Rangamati District|rangamati]], [[Chittagong District|chittagong]], [[Sylhet District|sylhet]], [[Kuakata|kuakata]] (Patuakhali), [[Sundarbans, The|sundarbans]] (Khulna). The 120-km long Cox's Bazar sea beach is considered to be the longest in the world. Kuakata is a unique beach for viewing sunrise as well as sun-setting. | ''Tourist spots'' [[Cox's Bazar|cox's bazar]], [[Rangamati District|rangamati]], [[Chittagong District|chittagong]], [[Sylhet District|sylhet]], [[Kuakata|kuakata]] (Patuakhali), [[Sundarbans, The|sundarbans]] (Khulna). The 120-km long Cox's Bazar sea beach is considered to be the longest in the world. Kuakata is a unique beach for viewing sunrise as well as sun-setting. | ||
''Population'' ( | ''Population'' (2022) total population 169.83 million; density 1,119 persons per sq km, annual growth rate' 1.22%, male-female ratio 98:100, urban population 31.51%, rural population 68.49%. Life expectancy at birth (2022) 72.4 years. At the point of ethnicity Bangladeshi people are amalgamation of Dravidian, Proto-Australoaid, Mongoloid, and Ariyan. Tribal people with a population of just over 1.2 million occupy mainly khagrachhari, bandarban, Rangamati, Chittagong, Cox’s Bazar, habiganj, Sylhet, sunamganj, maulvi bazar, dinajpur, joypurhat, Rajshahi, naogaon, rangpur, bogra, nawabganj, mymensingh, netrokona, barguna and bhola districts. There are some 45 tribal groups in Bangladesh and among those chakma, garo, hajong, khasia, magh, santals, rakhain, manipuri, murong are notable. | ||
''Religion'' Muslims | ''Religion'' (2022) Muslims 91.04%, Hindus 7.95%, Buddhists 0.61%, Christian 0.3% and others 0.1%. | ||
''Language'' National Language: Bangla (99.5% speak Bangla and 0.5% other dialects). English is the second most important language. | ''Language'' National Language: Bangla (99.5% speak Bangla and 0.5% other dialects). English is the second most important language. | ||
''Literacy'' (7 years and above) | ''Literacy'' (7 years and above) 74.66% (2022). | ||
''Educational institutions'' Public university ( | ''Educational institutions'' Public university (2022) 57, private university (2022) 113, government medical college 37, private medical college 72 (2022), engineering college 8, polytechnic institute 20, college (general education) 3340 (2022), secondary school 18,756 and primary school 82,218 (2022). | ||
''Health facilities'' ( | ''Health facilities'' (2022) Hospitals 2,860; hospital beds 74,415; registered physician 49,994; households per physician 1,847; | ||
''Employment and occupation'' (Labour Force Survey 2002-03, in percent) technical and professional 3.8; administrative and managerial 0.2; clerical works 3.4; sales works 14.8; service works 4.5; agriculture, forestry and fisheries 51.4; production and transport 21.9. | ''Employment and occupation'' (Labour Force Survey 2002-03, in percent) technical and professional 3.8; administrative and managerial 0.2; clerical works 3.4; sales works 14.8; service works 4.5; agriculture, forestry and fisheries 51.4; production and transport 21.9. | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
''Energy sources'' Fuelwood, natural gas, liquid petroleum fuels, coal, hydropower, solar power, [[Biogas|biogas]], etc. | ''Energy sources'' Fuelwood, natural gas, liquid petroleum fuels, coal, hydropower, solar power, [[Biogas|biogas]], etc. | ||
''Financial system'' one central bank ([[Bangladesh Bank|bangladesh bank]]), | ''Financial system'' one central bank ([[Bangladesh Bank|bangladesh bank]]), 61 commercial banks (6 nationalised commercial banks or NCBs), 46 private domestic banks and 9 foreign banks), 5 state-owned specialised banks, also known as development finance institutions (DFIs), 23 non-bank financial institutions, 27 merchant bankers, 556 money changers, the Investment Corporation of Bangladesh (ICB), 2 stock exchanges (the [[Dhaka Stock Exchange, The|dhaka stock exchange]] and [[Chittagong Stock Exchange|chittagong stock exchange]]), 2 state-owned and 39 private sector insurance companies, about 10 leasing companies, Post Office Savings Bank and the Postal Life Insurance schemes. There are 145,000 co-operatives. Bangladesh Samabaya Bank Ltd is the apex institution of the co-operative sector. There are over 1,200 non-governmental and non-profit micro finance institutions. | ||
''Industries'' Jute, tea, [[Textiles|textile]], garments, [[Paper|paper]], newsprint, [[Fertiliser|fertiliser]], leather and leather goods, cement, sugar, fish processing, pharmaceuticals and chemicals. | ''Industries'' Jute, tea, [[Textiles|textile]], garments, [[Paper|paper]], newsprint, [[Fertiliser|fertiliser]], leather and leather goods, cement, sugar, fish processing, pharmaceuticals and chemicals. | ||
| Line 64: | Line 64: | ||
''Foreign trade'' Export: 16.20 billion US$; Import: 23.74 billion US$ (2009-10). | ''Foreign trade'' Export: 16.20 billion US$; Import: 23.74 billion US$ (2009-10). | ||
''Currency'' Taka (Tk | ''Currency'' Taka (Tk 105 = US$1, December 2022). | ||
''Per-capita income'''US$ | ''Per-capita income'''US$ 2,687 (2022). | ||
''Transport and communication'' Metalled road | ''Transport and communication'' Metalled road 21,595 km; Railways 2,955.53 km. Waterways 8,900 km. | ||
''Major bridges'' [[ | ''Major bridges'' [[Padma Bridge|padma bridge]] opened in 25 June 2022 with a length of 6.15 km; [[Bangabandhu Jamuna Multipurpose Bridge|bangabandhu jamuna multipurpose bridge]]; Japan-Bangladesh Friendship Bridge (on the Meghna river at Gazaria upazila, Munshiganj); Bangladesh-UK Friendship Bridge (on the Meghna river at Bhairab upazila, Kishoreganj district) Meghna-Gumti Bridge (on the Meghna river at Daudkandi upazila, Comilla); Tarra Bridge (on the Dhaleshwari river at Ghior upazila, Manikganj); China-Bangladesh Friendship Bridge 1 (on the Buriganga river in Dhaka); China-Bangladesh Friendship Bridge 2 (on the Buriganga river in Dhaka); Shitalakshya Bridge, popularly known as Kanchpur Bridge (on the Shitalakshya river at Sonargaon upazila, Narayanganj); [[Karnafuli Bridge|karnafuli bridge]] (on the Karnafuli river at Chandgaon upazila, Chittagong) are notable. | ||
''Railway bridges'' [[Hardinge Bridge|hardinge bridge]] (on the Ganges river at Ishwardi upazila, pabna), Bhairab Bridge (on the Meghna river at [[Bhairab River|bhairab]] upazila, [[Kishoreganj District|kishoreganj]]); Tista Bridge (on the Tista river at [[Kaunia Upazila|kaunia]] upazila, Rangpur) are notable. | ''Railway bridges'' [[Hardinge Bridge|hardinge bridge]] (on the Ganges river at Ishwardi upazila, pabna), Bhairab Bridge (on the Meghna river at [[Bhairab River|bhairab]] upazila, [[Kishoreganj District|kishoreganj]]); Tista Bridge (on the Tista river at [[Kaunia Upazila|kaunia]] upazila, Rangpur) are notable. | ||
Latest revision as of 04:59, 4 March 2024
Bangladesh emerged as an independent and sovereign country on 16 December 1971 following a nine-month war of liberation. Dhaka (previously spelt Dacca) is its capital.
Information Brief
Official name People's Republic of Bangladesh (Gana Prajatantri Bangladesh).
Capital Dhaka.
Government Parliamentary form of government, president is head of the State and prime minister is head of government.
UNO member UNO membership no 136, admitted on 17 September, 1974.
Geographical location In South Asia, between 20°34' to 26°38' north latitude and 88°01' to 92°41' east longitude. Maximum extension is about 440 km in E-W direction and 760 km in NNW-SSE direction.
Time GMT +6.00 hours.
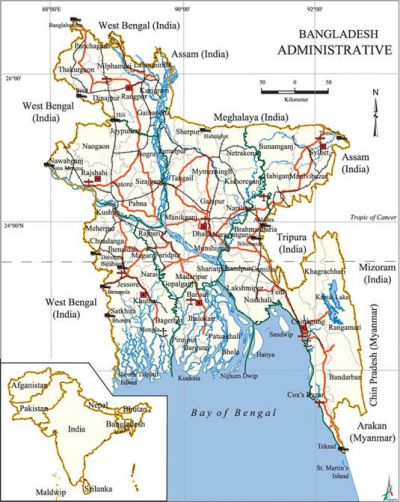
Area and boundaries Area: 147,570 sq km. Boundaries: west bengal (India) on the west; West Bengal, assam and Meghalaya (all the Indian states) on the north; Indian states of Assam, tripura and Mizoram together with Myanmar on the east; and bay of bengal on the south. The total length of the land border is about 4,246 km, of which 93.9% is shared with India and the rest 6% with Myanmar. Limit of territorial water is 12 nautical miles (22.22 km) and the area of the high seas extending to 200 nautical miles (370.40 km) measured from the baselines constitutes the Exclusive Economic Zone (EEZ).
Administrative units division 8 (dhaka, chittagong, khulna, rajshahi, barisal, sylhet, rangpur and Mymensingh); district 64; upazila 495 and thana 652 (2022), union 4,578 (2022), mouza 59,990, village 87,362; city corporation 12 (Dhaka North City Corporation, Dhaka South City Corporation, chittagong city corporation, khulna city corporation, rajshahi city corporation, sylhet city corporation, barisal city corporation, Rangpur City Corporation, Mymensingh City Corporation, narayanganj city corporation, comilla city corporation, Gazipur City Corporation); municipality 331 (2022).
Physiography A humid lowlying alluvial region, Bangladesh is composed mainly of the great combined delta of the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna rivers. It is one of the largest deltas in the world. The monotony of flatness has been relieved inland by two elevated tracts - the madhupur and the barind tracts, and on the northeast and southeast by rows of hills. Some 75% of the land is less than 3m above mean sea level (MSL) and vulnerable to floods and cyclones. The maximum elevation is 1,280m above MSL at Saichal Range in rangamati district. Tajingdong is the highest peak and called as Bijoy.
Rivers Total rivers including tributaries and distributaries are about 700 under three mighty river systems: ganges-padma river system, brahmaputra-jamuna river system and surma-meghna river system. Rivers of the southeastern hilly region are considered as the chittagong region river system. Principal rivers are: ganges, padma, brahmaputra, jamuna, surma, kushiyara, meghna, karnafuli, old brahmaputra, arial khan, buriganga, shitalakshya, tista, atrai, gorai, madhumati, kobadak, rupsa-pashur, feni.
Climate Sub-tropical monsoon. Average maximum and minimum winter temperatures are 29°C and 11°C respectively; average maximum and minimum summer temperatures are 34°C and 21°C respectively. Annual rainfall 1,194 mm to 3,454 mm. Highest humidity 80% to 100% (August-September), lowest 36% (February-March).
Archaeological sites paharpur (5 km west of Jamalganj railway station in Joypurhat district, actually the site includes the Badalgachi upazila of Naogaon district), mahasthangarh (about 12 km north of Bogra town, the site includes partly Shibganj and partly Bogra Sadar upazilas of Bogra district), bhasu vihara (about 4.8-6.4 km northwest of Mahasthangarh), mainamati (8 km west of Comilla town), halud vihara (about 14.5 km west-south-west of Paharpur), sitakot vihara (Nawabganj upazila of Dinajpur district), wari-bateshwar (Narsingdi).
Tourist spots cox's bazar, rangamati, chittagong, sylhet, kuakata (Patuakhali), sundarbans (Khulna). The 120-km long Cox's Bazar sea beach is considered to be the longest in the world. Kuakata is a unique beach for viewing sunrise as well as sun-setting.
Population (2022) total population 169.83 million; density 1,119 persons per sq km, annual growth rate' 1.22%, male-female ratio 98:100, urban population 31.51%, rural population 68.49%. Life expectancy at birth (2022) 72.4 years. At the point of ethnicity Bangladeshi people are amalgamation of Dravidian, Proto-Australoaid, Mongoloid, and Ariyan. Tribal people with a population of just over 1.2 million occupy mainly khagrachhari, bandarban, Rangamati, Chittagong, Cox’s Bazar, habiganj, Sylhet, sunamganj, maulvi bazar, dinajpur, joypurhat, Rajshahi, naogaon, rangpur, bogra, nawabganj, mymensingh, netrokona, barguna and bhola districts. There are some 45 tribal groups in Bangladesh and among those chakma, garo, hajong, khasia, magh, santals, rakhain, manipuri, murong are notable.
Religion (2022) Muslims 91.04%, Hindus 7.95%, Buddhists 0.61%, Christian 0.3% and others 0.1%.
Language National Language: Bangla (99.5% speak Bangla and 0.5% other dialects). English is the second most important language.
Literacy (7 years and above) 74.66% (2022).
Educational institutions Public university (2022) 57, private university (2022) 113, government medical college 37, private medical college 72 (2022), engineering college 8, polytechnic institute 20, college (general education) 3340 (2022), secondary school 18,756 and primary school 82,218 (2022).
Health facilities (2022) Hospitals 2,860; hospital beds 74,415; registered physician 49,994; households per physician 1,847;
Employment and occupation (Labour Force Survey 2002-03, in percent) technical and professional 3.8; administrative and managerial 0.2; clerical works 3.4; sales works 14.8; service works 4.5; agriculture, forestry and fisheries 51.4; production and transport 21.9.
Artisans kamar (blacksmith), kumar (potter), tanti (weaver), modak or moyra (sweetmeat maker), sutradhar or chutar (carpenter), kalu (oil presser), kansaru (brazier), shankhari (shell cutter), swarnakar (goldsmith), gharami (house builder), kahar (palanquin bearer), karati (sawyer), patial(matmaker).
Mineral resources natural gas, coal, peat, limestone, hardrock, beach sand heavy mineral (zircon, rutile, Ilmenite, Garnet, Magnetite, Monazite, Leucoxene, Kyanite), glass sand, white clay, brick clay and metallic minerals.
Water resources Bangladesh is endowed with plenty of surface water and groundwater resources. Surface water inflows of the country vary from a maximum of about 140,000 cumec in August to a minimum of about 7,000 cumec in February. The alluvial aquifer systems of Bangladesh are some of the most productive groundwater reservoirs. Groundwater in Bangladesh occurs at a very shallow depth where the recent river-borne sediments form prolific aquifers in the floodplains. In the higher terraces, the Barind and Madhupur tracts, the Pleistocene Dupi Tila sands act as aquifers. In the hilly areas, the Pliocene Tipam sands serve as aquifers. The groundwater table over most of Bangladesh lies very close to the surface and fluctuates with the annual recharge discharge conditions.
Energy sources Fuelwood, natural gas, liquid petroleum fuels, coal, hydropower, solar power, biogas, etc.
Financial system one central bank (bangladesh bank), 61 commercial banks (6 nationalised commercial banks or NCBs), 46 private domestic banks and 9 foreign banks), 5 state-owned specialised banks, also known as development finance institutions (DFIs), 23 non-bank financial institutions, 27 merchant bankers, 556 money changers, the Investment Corporation of Bangladesh (ICB), 2 stock exchanges (the dhaka stock exchange and chittagong stock exchange), 2 state-owned and 39 private sector insurance companies, about 10 leasing companies, Post Office Savings Bank and the Postal Life Insurance schemes. There are 145,000 co-operatives. Bangladesh Samabaya Bank Ltd is the apex institution of the co-operative sector. There are over 1,200 non-governmental and non-profit micro finance institutions.
Industries Jute, tea, textile, garments, paper, newsprint, fertiliser, leather and leather goods, cement, sugar, fish processing, pharmaceuticals and chemicals.
Export Processing Zone (EPZ) Existing: Chittagong EPZ (1983) and Dhaka EPZ. Proposed: Gazipur, Mongla, Ishwardi, Comilla, Saidpur and Sirajganj. The government has signed an agreement with the Republic of Korea to establish a Korean EPZ in Chittagong.
Exports Ready made garments, raw jute, jute manufactures, tea, leather and leather products, frozen shrimps and other fish products, newsprint, handicraft.
Imports Wheat, oil seeds, crude petroleum, raw cotton, edible oil, petroleum products, fertiliser, cement, yarn.
Foreign trade Export: 16.20 billion US$; Import: 23.74 billion US$ (2009-10).
Currency Taka (Tk 105 = US$1, December 2022).
Per-capita income'US$ 2,687 (2022).
Transport and communication Metalled road 21,595 km; Railways 2,955.53 km. Waterways 8,900 km.
Major bridges padma bridge opened in 25 June 2022 with a length of 6.15 km; bangabandhu jamuna multipurpose bridge; Japan-Bangladesh Friendship Bridge (on the Meghna river at Gazaria upazila, Munshiganj); Bangladesh-UK Friendship Bridge (on the Meghna river at Bhairab upazila, Kishoreganj district) Meghna-Gumti Bridge (on the Meghna river at Daudkandi upazila, Comilla); Tarra Bridge (on the Dhaleshwari river at Ghior upazila, Manikganj); China-Bangladesh Friendship Bridge 1 (on the Buriganga river in Dhaka); China-Bangladesh Friendship Bridge 2 (on the Buriganga river in Dhaka); Shitalakshya Bridge, popularly known as Kanchpur Bridge (on the Shitalakshya river at Sonargaon upazila, Narayanganj); karnafuli bridge (on the Karnafuli river at Chandgaon upazila, Chittagong) are notable.
Railway bridges hardinge bridge (on the Ganges river at Ishwardi upazila, pabna), Bhairab Bridge (on the Meghna river at bhairab upazila, kishoreganj); Tista Bridge (on the Tista river at kaunia upazila, Rangpur) are notable.
Major inland riverports Dhaka, Chandpur, Barisal, Khulna, Narayanganj, Bhairab Bazar, Ashuganj, Sirajganj.
Seaports Chittagong Port and Mongla Port.
Airports Zia International Airport, Dhaka; Amanat Shah International Airport, Chittagong; Osmany Airport, Sylhet; Cox's Bazar Airport; Jessore Airport; Barisal Airport; Rajshahi Airport; Saidpur Airport, Nilphamari; Ishwardi Airport, Pabna; Tejgaon STOL Port, Dhaka; Shamsernagar STOL Port, Maulvi Bazar; Comilla STOL Port, comilla; Lalmonirhat STOL Port; Thakurgaon STOL Port.
Radio stations Dhaka, Chittagong, Khulna, Rajshahi, Rangpur, Sylhet, Rangamati, Comilla and Thakurgaon.
TV stations Transmission centres: Dhaka and Chittagong. Relay stations: Chittagong, Sylhet, Khulna, Natore, Mymensingh, Rangpur, Noakhali, Satkhira, Cox's Bazar, Rangamati and Thakurgaon.
Satellite station Three communication satellite ground receiving stations: Betbunia, Chittagong; Talibabad, Savar, Dhaka, Mohakhali, Dhaka.
Food Staple diet: rice, wheat, vegetable, pulses, fish and meat.
Principal crops jute, rice, wheat, potato, tea, tobacco, sugarcane.
Principal fruits mango (am), jackfruit (kanthal), black berry (jam), pineapple (anarax), banana (kala), litchi (lichu), lemon (lebu), guava (peyara), papaya (pepe), tamarind (tentul), watermelon (tarmuj), rose apple (jamrul), jujube (badai).
Principal fishes Freshwater fishes: hilsa (Ilix) [Tenualosa ilisha]; carps (Rui, Catla, Mrigal, Kalibaux, etc); barbs (Punti, Mahaxol, etc); minnows (Darkina, Chela, Mola, etc); catfishes (Tebgra, Aid, Shingi, Magur, etc); Climbing Perch (Koi), [Anabas testudineus]. Saline water fishes: Jew fishes (Poa), thread-fins (Tapasi), mullets (Bata), pomfrets (Rupchanda), etc.
Flora 6000 species (5000 flowering plants).
Fauna Vertebrates: about 1600 species; fish: 266 inland species and 442 marine species; amphibians: 22 species; reptiles 126 species (109 inland and 17 marine); birds: 628 species (388 resident and 240 migratory); mammals: 113 species (110 inland and 3 marine).
Forest Total 21403 sq km. Hill forest land 13,617 sq km; Inland forest land 1,220 sq km; Littoral forest 6,566 sq km.
National days Shaheed Dibas (Martyrs' Day) on 21 February now observed as international mother language day; Swadhinata Dibas (independence day) on 26 March; pahela baishakh or Bangla Nababarsa (Bangla New Year); Bijoy Dibas (victory day) on 16 December.
Festivals Common: Navanna, pahela baishakh (Bangla Nababarsha). Religious: Muslim eid-ul fitr, eid-ul azha, shab-e-qadr, shab-e-barat, Eid-e-Miladunnabi, muharram; Hindu durga puja, kali puja, laksmi puja, Saraswati puja, Doljatra, Holi; Christian christmas; Buddhist buddha purnima.
Games kabadi is the national game; football, cricket, hockey, tennis, badminton, volleyball, handball, chess and carom are also popular games.
National flower Shapla or water lily (Nymphaea pubescens).
National fruit Kanthal or jackfruit (Artocarpus heterophyllus).
National bird Doel or magpie-robin or Oriental Magpie Robin (Copsychus saularis).
National fish Ilish hilsa (Tenualosa ilisha).
National animal Bagh or bengal tiger, well known as Royal Bengal Tiger (Pathera tigris). [Masud Hasan Chowdhury]
