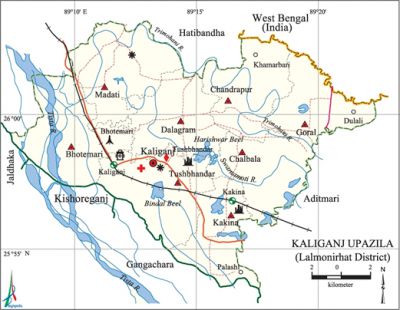
Kaliganj Upazila (Lalmonirhat District)
Kaliganj Upazila (lalmonirhat district) area 253.23 sq km, located in between 25°54' and 26°04' north latitudes and in between 89°07' and 89°22' east longitudes. It is bounded by hatibandha upazila and west bengal of India on the north, gangachara and aditmari upazilas on the south, Aditmari upazila on the east, kishoreganj (nilphamari) and jaldhaka upazilas on the west.
Population Total 245595; male 122225, female 123370; Muslim 199007, Hindu 46308, Buddhist 1, Christian 191 and others 88.
Water bodies Main rivers: tista, Trimohani, Swarnamoti; Harishwar and Bindal beels are notable.
Administration Kaliganj Thana, now an upazila, was formed in 1913.
| Upazila | ||||||||
| Municipality | Union | Mouza | Village | Population | Density (per sq km) | Literacy rate (%) | ||
| Urban | Rural | Urban | Rural | |||||
| - | 8 | 64 | 92 | 18967 | 226628 | 970 | 55.6 | 45.2 |
| Upazila Town | ||||||||
|
Area |
Mouza |
Population |
Density |
Literacy rate (%) | ||||
| 6.17 | 3 | 18967 | 3074 | 55.6 | ||||
| Union | ||||
| Name of union and GO code | Area (acre) | Population | Literacy rate (%) | |
| Male | Female | |||
| Kakina 53 | 5968 | 16260 | 15987 | 45.2 |
| Goral 47 | 5465 | 10382 | 10740 | 43.6 |
| Chandrapur 29 | 6977 | 15553 | 16096 | 47.0 |
| Chalbala 23 | 7026 | 13045 | 13317 | 51.5 |
| Tushbhandar 95 | 8406 | 24170 | 23844 | 51.1 |
| Dalagram 35 | 7055 | 13832 | 14067 | 45.9 |
| Bhotemari 17 | 13139 | 12233 | 12086 | 32.8 |
| Madati 65 | 8540 | 16750 | 17233 | 45.0 |
Source Bangladesh Population Census 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics.
Archaeological heritage and relics Rajbari of Maharaja Mahima Ranjan (Kakina), Tushbhandar Rajbari (Tushbhandar), Sambhusagar, the house and statue of Daribabu.
Historical events Main historical events of the upazila include invasion of Kuchbihar by the Mughal in 1687, peasant rebellion led by Nuraldin, Fakir-Sannyasi rebellion and the peasant movement in the 1940.
War of Liberation During the war of liberation in 1971 Kaliganj Upazila was under Sector 6. On 6 April the Pak army launched a surprise attack on Kaliganj and brutally killed a number of people. The Pak army was forced to leave Kaliganj in the face of heavy attack on them by the freedom fighters launched on 5 and 6 December. Kaliganj was liberated on 6 December. There is a mass grave at a place adjacent to the KUP Degree College and a mass killing site on the east of Bhotemari Railway Station; a memorial monument ("Chiranjibi Kaliganj") was established at the compound of Kaliganj KUP High School.
For details: see কালীগঞ্জ উপজেলা (লালমনিরহাট জেলা), বাংলাদেশ মুক্তিযুদ্ধ জ্ঞানকোষ (Encyclopedia of Bangladesh War of Liberation), বাংলাদেশ এশিয়াটিক সোসাইটি, ঢাকা ২০২০, খণ্ড ২।
Religious institutions Ijaradar Mosque, Kakina Shib Mandir, Sree Sree Bhabatarini Kali Mandir, Bhagabateshwar Shib Mandir, Shib Mandir built by Zamindar Ananga Mahan are notable.
Literacy rate and educational institutions Average literacy 46.0%; male 48.9%, female 43.1%. Educational institutions: college 7, secondary school 39, primary school 130, madrasa 74. Noted educational institutions: Karim Uddin Public Degree College (1972), Uttar Bangla Degree College (1994), Tushbhandar Women's College (1998), Tushbhandar RMMP Government High School (1867), Kakina Mahima Ranjan Memorial Bilateral High School (1901), Dalagram Bilateral' High School' (1916), Karim Uddin Public Pilot High School (1959), Tushbhandar Nasar Uddin Government Girls' School (1968), 'Madanpur Bairati Government Primary School (1865), Kashiram Ekramia Senior Madrasa (1968).
Newspapers and periodicals Weekly: Rangapur Dikprakash (1848); monthly: Prottasha (defunct), Basana (1908).
Cultural organisations Library 44, club 50, cultural organisation 1, cinema hall 3, theatre stage 1, women's organisation 4.
Tourist spots Kakina Zamindar Bari, museum of Zamindar Mahima Ranjan (Kakina), house of Sheikh Fazlul Karim (Kakina), Tushbhandar Zamindar Bari (Tushbhandar).
Main sources of income Agriculture 76.42%, non-agricultural labourer 4.25%, industry 0.27%, commerce 8.83%, transport and communication 1.45%, service 3.30%, construction 0.54%, religious service 0.15%, rent and remittance 0.08% and others 4.71%.
Ownership of agricultural land Landowner 60.12%, landless 39.88%; agricultural landowner: urban 42.77% and rural 61.49%.
Main crops Paddy, wheat, tobacco, jute, potato, ginger.
Extinct or nearly extinct crops Linseed, aus paddy, millet, pulse, bajra. Main fruits Mango, jackfruit, banana, litchi, papaya, watermelon.
Communication facilities Pucca road 110 km, semi-pucca road 7 km, mud road 573 km; waterway 17 km; railway 20 km.
Extinct or nearly extinct traditional transport Palanquin, horse carriage, bullock cart.
Noted manufactories Flour mill, saw mill, ice factory, welding factory.
Cottage industries Goldsmith, weaving, potteries, blacksmith, wood work, bamboo work.
Hats, bazars and fairs Hats and bazars are 20, fairs 7, most noted of which are Kaliganj Hat, Chapar Hat, Chamtar Hat, Vullar Hat, Chowdhury Hat; Cowaghat Mela and Baruni Mela.
Main exports Tobacco, paddy, flour.
Access to electricity All the unions of the upazila are under rural electrification net-work. However 15.1% of the dwelling households have access to electricity.
Natural resources Stone with high quality silicate and manganese have been discovered in this upazila.
Sources of drinking water Tube-well 98.2%, tap 0.2% and others 1.6%.
Sanitation 73.2% of dwelling households of the upazila use sanitary latrines and 18.6% of dwelling households use non-sanitary latrines; 8.2% of households do not have latrine facilities.
Health centres Upazila health centre 1, union health centre 2. NGO activities Operationally important.
NGO activities brac, asa, Hitoshi Bangladesh, RDRS. [Md. Haider Ali Babu]
References Bangladesh Population Census 2001 and 2011, Bangladesh Bureau of Statistics; Cultural survey report of Kaliganj Upazila 2007.
